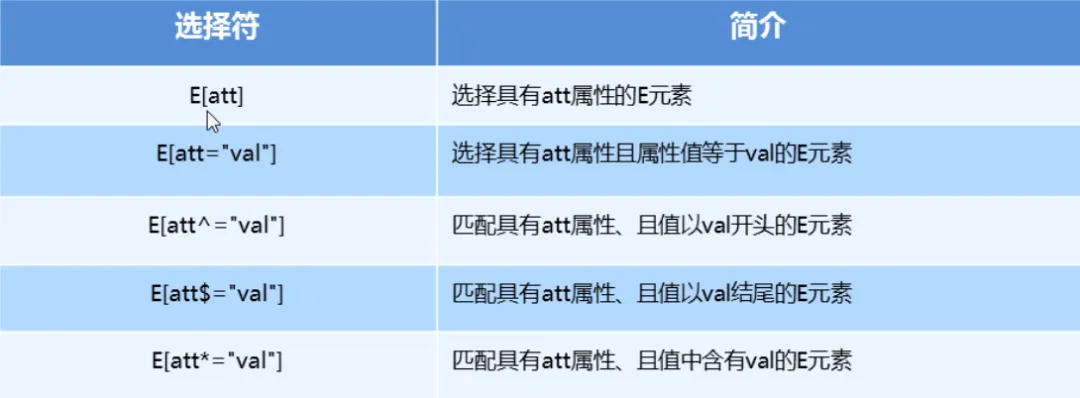
「1. CSS3属性选择器」
button {
cursor: pointer;
}
button[disabled] {
cursor: default;
}
input[type=search] {
color: skyblue;
}
span[class^=black] {
color: lightgreen;
}
span[class$=black] {
color: lightsalmon;
}
span[class*=black] {
color: lightseagreen;
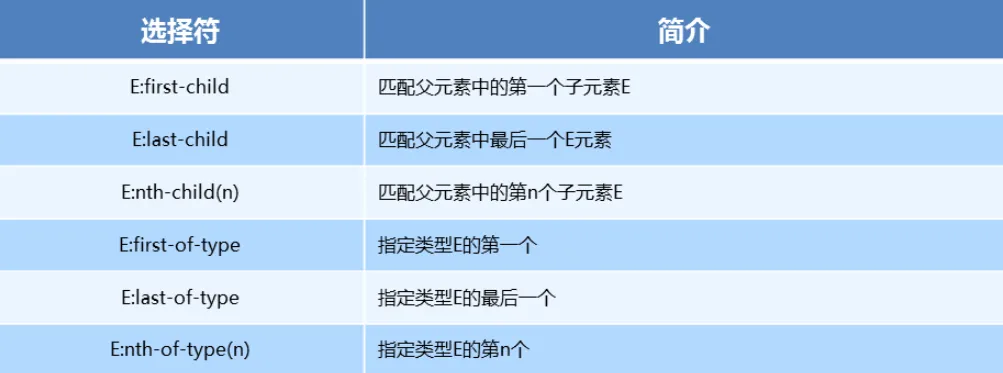
}「2. 结构伪类选择器」
ul li:first-child {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
ul li:last-child {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
ul li:nth-child(3) {
background-color: aqua;
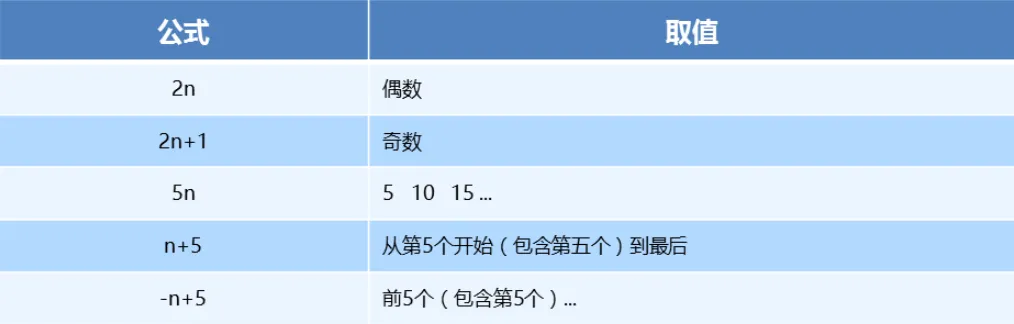
}nth-child(n) 参数n详解
注意:本质上就是选中第几个子元素
n 可以是数字、关键字、公式
n 如果是数字,就是选中第几个
常见的关键字有
even偶数、odd奇数常见的公式如下(如果 n 是公式,则从 0 开始计算)
但是第 0 个元素或者超出了元素的个数会被忽略
<style>
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(even) {
background-color: aquamarine;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
/*n 是公式,从 0 开始计算 */
ul li:nth-child(n) {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n) {
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n + 1) {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
/* 选择第 0 5 10 15, 应该怎么选 */
ul li:nth-child(5n) {
background-color: orangered;
}
/* n + 5 就是从第5个开始往后选择 */
ul li:nth-child(n + 5) {
background-color: peru;
}
/* -n + 5 前五个 */
ul li:nth-child(-n + 5) {
background-color: tan;
}
</style>nth-child与nth-of-type区别nth-child选择父元素里面的第几个子元素,不管是第几个类型nth-of-type选择指定类型的元素
<style>
div :nth-child(1) {
background-color: lightblue;
}
div :nth-child(2) {
background-color: lightpink;
}
div span:nth-of-type(2) {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
div span:nth-of-type(3) {
background-color: #fff;
}
</style>「3. 伪元素选择器」

伪元素选择器注意事项
before和after必须有content属性before在内容前面,after 在内容后面before和after创建的是一个元素,但是属于行内元素创建出来的元素在
Dom中查找不到,所以称为伪元素伪元素和标签选择器一样,权重为 1
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid lightcoral;
}
div::after,
div::before {
width: 20px;
height: 50px;
text-align: center;
display: inline-block;
}
div::after {
content: '德';
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
div::before {
content: '道';
background-color: mediumaquamarine;
}
</style>伪元素字体图标
p {
position: relative;
width: 220px;
height: 22px;
border: 1px solid lightseagreen;
margin: 60px;
}
p::after {
content: '\ea50';
font-family: 'icomoon';
position: absolute;
top: -1px;
right: 10px;
}「4. 2D 转换之translate」
2D转换
2D转换是改变标签在二维平面上的位置和形状
移动:translate
旋转:rotate
缩放:scale
translate语法
x就是X轴上水平移动
y就是y轴上水平移动
transform: translate(x, y)
transform: translateX(n)
transfrom: translateY(n) 重点知识点
2D的移动主要是指水平、垂直方向上的移动
translate最大的优点就是不影响其他元素的位置
translate中的100%单位,是相对于本身的宽度和高度来进行计算的
行内标签没有效果
div {
background-color: lightseagreen;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
/* 平移 */
/* 水平垂直移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(100px, 100px); */
/* 水平移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(100px, 0) */
/* 垂直移动 100px */
/* transform: translate(0, 100px) */
/* 水平移动 100px */
/* transform: translateX(100px); */
/* 垂直移动 100px */
transform: translateY(100px);
/*百分比用法*/
transform: translateY(100%);
}让一个盒子水平垂直居中
div {
position: relative;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: pink;
/* 1. 我们tranlate里面的参数是可以用 % */
/* 2. 如果里面的参数是 % 移动的距离是 盒子自身的宽度或者高度来对比的 */
/* 这里的 50% 就是 50px 因为盒子的宽度是 100px */
/* transform: translateX(50%); */
}
p {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
/1.* margin-top: -100px;
margin-left: -100px; */
/2.* translate(-50%, -50%)
盒子往上走自己高度的一半 */
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
span {
/* translate 对于行内元素是无效的 */
transform: translate(300px, 300px);
}「5. 2D 转换之rotate」
rotate旋转
2D旋转指的是让元素在二维平面内顺时针或者逆时针旋转
/* 单位是:deg */
img:hover {
transform: rotate(360deg)
}rotate语法
rotate里面跟度数,单位是deg角度为正时,顺时针,角度为负时,逆时针
默认旋转的中心点是元素的中心点
设置元素旋转的中心的(transform-origin)
transform-origin: x y;注意后面的参数 x 和 y 用空格隔开
x y 默认旋转的中心点是元素的中心(50% 50%),等价于center center
还可以给x y 设置像素或者方位名词(top、bottom、left、right、center)
「6. 2D 转换之scale」
scale的作用:用来控制元素的放大与缩小
transform: scale(x, y)知识要点:注意,x与y之间用逗号进行分隔
transform: scale(1, 1): 宽高都放大一倍,相当于没有放大transform: scale(2, 2): 宽和高都放大了二倍transform: scale(2): 如果只写了一个参数,第二个参数就和第一个参数一致transform:scale(0.5, 0.5): 缩小scale最大的优势:可以设置转换中心点缩放,默认以中心点缩放,而且不影响其他盒子
div:hover {
/* 注意,数字是倍数的含义,所以不需要加单位 */
/* transform: scale(2, 2) */
/* 实现等比缩放,同时修改宽与高 */
/* transform: scale(2) */
/* 小于 1 就等于缩放*/
transform: scale(0.5, 0.5)
}「7. 2D 转换综合写法以及顺序问题」
知识要点
同时使用多个转换,其格式为
transform: translate() rotate() scale()顺序会影响到转换的效果(先旋转会改变坐标轴方向)
当我们同时有位置或者其他属性的时候,要将位移放到最前面
div:hover {
transform: translate(200px, 0) rotate(360deg) scale(1.2)
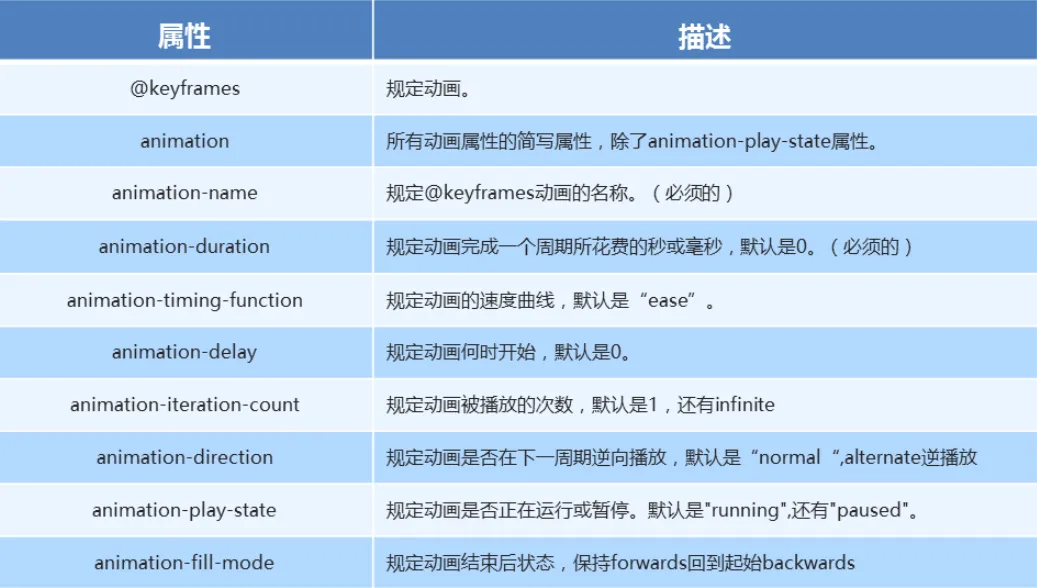
}动画(animation)
**「动画」**是CSS3中最具颠覆性的特征之一,可通过设置多个节点来精确的控制一个或者一组动画,从而实现复杂的动画效果。
「动画的使用」
先定义动画
再调用定义好的动画
/*1. 定义动画*/
@keyframes 动画名称 {
0% {
width: 100px;
}
100% {
width: 200px
}
}
div {
/* 调用动画 */
animation-name: 动画名称;
/* 持续时间 */
animation-duration: 持续时间;
}「动画序列」
0% 是动画的开始,100 % 是动画的完成,这样的规则就是动画序列
在 @keyframs中规定某项 CSS 样式,就由创建当前样式逐渐改为新样式的动画效果
动画是使元素从一个样式逐渐变化为另一个样式的效果,可以改变任意多的样式任意多的次数
用百分比来规定变化发生的时间,或用
from和to,等同于 0% 和 100%
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aquamarine;
animation-name: move;
animation-duration: 0.5s;
}
@keyframes move{
0% {
transform: translate(0px)
}
100% {
transform: translate(500px, 0)
}
}
</style>「动画常见属性」
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aquamarine;
/* 动画名称 */
animation-name: move;
/* 动画花费时长 */
animation-duration: 2s;
/* 动画速度曲线 */
animation-timing-function: ease-in-out;
/* 动画等待多长时间执行 */
animation-delay: 2s;
/* 规定动画播放次数 infinite: 无限循环 */
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
/* 是否逆行播放 */
animation-direction: alternate;
/* 动画结束之后的状态 */
animation-fill-mode: forwards;
}
div:hover {
/* 规定动画是否暂停或者播放 */
animation-play-state: paused;
}「动画简写方式」
/* animation: 动画名称 持续时间 运动曲线 何时开始 播放次数 是否反方向 起始与结束状态 */
animation: name duration timing-function delay iteration-count direction fill-mode知识要点
简写属性里面不包含
animation-paly-state暂停动画
animation-paly-state: paused; 经常和鼠标经过等其他配合使用要想动画走回来,而不是直接调回来:
animation-direction: alternate盒子动画结束后,停在结束位置:
animation-fill-mode: forwards
animation: move 2s linear 1s infinite alternate forwards;「速度曲线细节」
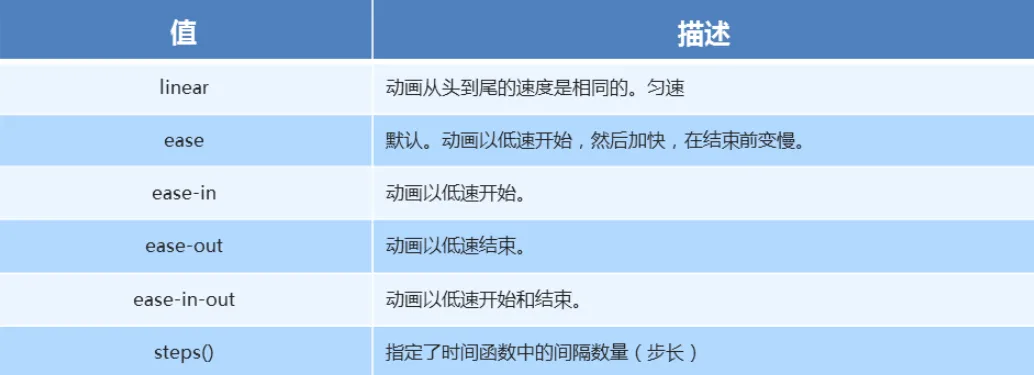
animation-timing-function: 规定动画的速度曲线,默认是ease
/*打字机效果*/
div {
width: 0px;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
white-space: nowrap;
overflow: hidden;
background-color: aquamarine;
animation: move 4s steps(24) forwards;
}
@keyframes move {
0% {
width: 0px;
}
100% {
width: 480px;
}
}CSS 过渡transition
通过过渡transition,可以让web前端开发人员不需要javascript就可以实现简单的动画交互效果。
深入理解CSS过渡transitionhttps://www.cnblogs.com/xiaohuochai/p/5347930.html
「定义」过渡transition是一个复合属性,包括transition-property、transition-duration、transition-timing-function、transition-delay这四个子属性。通过这四个子属性的配合来完成一个完整的过渡效果。
transition-property: 过渡属性(默认值为all)
transition-duration: 过渡持续时间(默认值为0s)
transiton-timing-function: 过渡函数(默认值为ease函数)
transition-delay: 过渡延迟时间(默认值为0s)
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: pink;
transition-duration: 3s;
/* 以下三值为默认值,稍后会详细介绍 */
transition-property: all;
transition-timing-function: ease;
transition-delay: 0s;
}
.test:hover{
width: 500px;
}
~~~html
<div class="test"></div>
复合属性过渡transition的这四个子属性只有是必需且不能为0。其中,和都是时间。当两个时间同时出现时,第一个是,第二个是;当只有一个时间时,它是,而为默认值0s
注意:
transition的这四个子属性之间不能用逗号隔开,只能用空格隔开。因为逗号隔开的代表不同的属性(transition属性支持多值,多值部分稍后介绍);而空格隔开的代表不同属性的四个关于过渡的子属性。
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: pink;
/*代表持续时间为2s,延迟时间为默认值0s*/
transition;2s;
}
.test:hover{
width: 500px;
}
<div class="test"></div>
延迟时间delay 案例
.test{
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: pink;
/*代表持续时间为1s,延迟时间为2s*/
transition: 1s 2s;
}
.test:hover{
width: 500px;
}
<div class="test"></div>
「过渡属性」
值: none | all | [,]
初始值: all
应用于: 所有元素
继承性: 无
none: 没有指定任何样式
all: 默认值,表示指定元素所有支持transition-property属性的样式
<transition-property>: 可过渡的样式,可用逗号分开写多个样式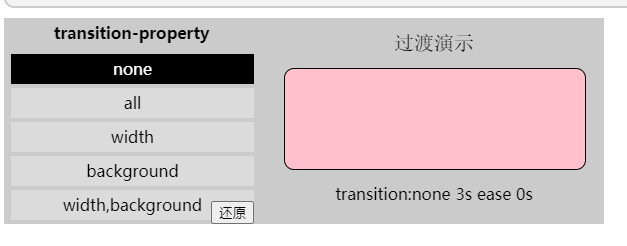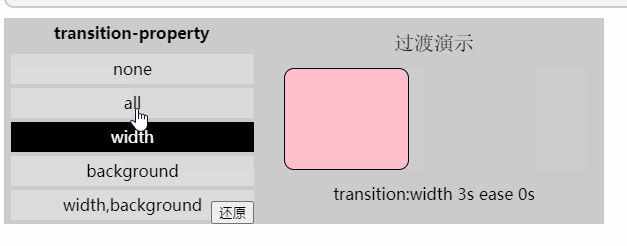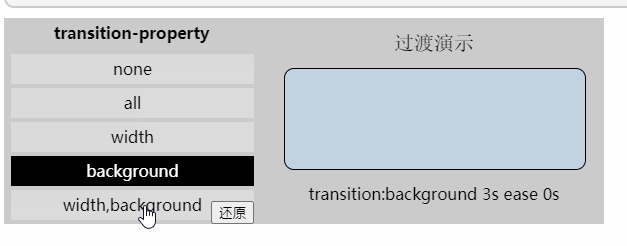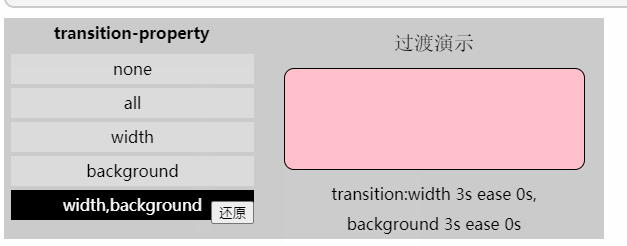
「过渡持续时间」
值: [,]*
初始值: 0s
应用于: 所有元素
继承性: 无
[注意]该属性不能为负值
[注意]若该属性为0s则为默认值,若为0则为无效值。所以必须带单位
[注意]该值为单值时,即所有过渡属性都对应同样时间;该值为多值时,过渡属性按照顺序对应持续时间
/*DEMO中的过渡属性值*/
transition-property: width,background;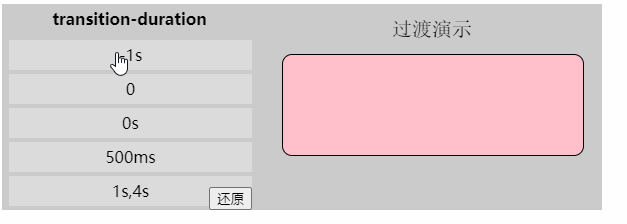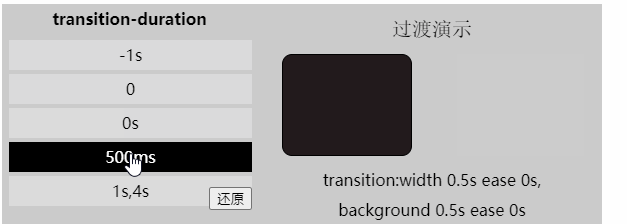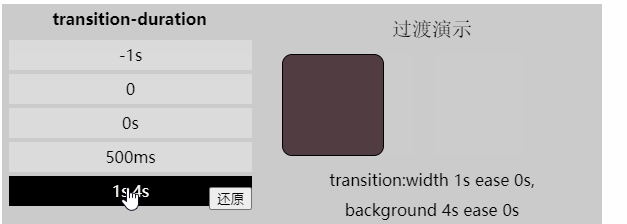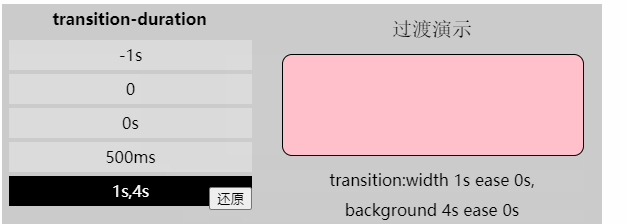 「过渡时间函数」
「过渡时间函数」
过渡时间函数用于定义元素过渡属性随时间变化的过渡速度变化效果
值: [,]*
初始值: ease
应用于: 所有元素
继承性: 无
取值 过渡时间函数共三种取值,分别是关键字、steps函数和bezier函数
关键字其实是bezier函数或steps函数的特殊值
ease: 开始和结束慢,中间快。
linear: 匀速。
ease-in: 开始慢。
ease-out: 结束慢。
ease-in-out: 和ease类似,但比ease幅度大。