索引管理
为什么我们要手动创建索引
直接put数据 PUT index/_doc/1,es会自动生成索引,并建立动态映射dynamic mapping。
在生产上,我们需要自己手动建立索引和映射,为了更好地管理索引。就像数据库的建表语句一样。
索引管理
创建索引
创建索引的语法
PUT /index
{
"settings": { ... any settings ... },
"mappings": {
"properties" : {
"field1" : { "type" : "text" }
}
},
"aliases": {
"default_index": {}
}
}举例:
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"field1":{
"type": "text"
},
"field2":{
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"aliases": {
"default_index": {}
}
}索引别名
插入数据
POST /my_index/_doc/1
{
"field1":"java",
"field2":"js"
}查询数据 都可以查到
GET /my_index/_doc/1
GET /default_index/_doc/1
查询索引
GET /my_index/_mapping
GET /my_index/_setting
修改索引
修改副本数
PUT /my_index/_settings
{
"index" : {
"number_of_replicas" : 2
}
}删除索引
DELETE /my_index
DELETE /index_one,index_two
DELETE /index_*
DELETE /_all
为了安全起见,防止恶意删除索引,删除时必须指定索引名:
elasticsearch.yml
action.destructive_requires_name: true
定制分词器
默认的分词器
standard
分词三个组件,character filter,tokenizer,token filter
standard tokenizer:以单词边界进行切分
standard token filter:什么都不做
lowercase token filter:将所有字母转换为小写
stop token filer(默认被禁用):移除停用词,比如a the it等等
修改分词器的设置
启用english停用词token filter
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"es_std": {
"type": "standard",
"stopwords": "_english_"
}
}
}
}
}测试分词
GET /my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "a dog is in the house"
}
GET /my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "es_std",
"text":"a dog is in the house"
}定制化自己的分词器
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"char_filter": {
"&_to_and": {
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": ["&=> and"]
}
},
"filter": {
"my_stopwords": {
"type": "stop",
"stopwords": ["the", "a"]
}
},
"analyzer": {
"my_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": ["html_strip", "&_to_and"],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase", "my_stopwords"]
}
}
}
}
}测试
GET /my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "my_analyzer",
"text": "tom&jerry are a friend in the house, <a>, HAHA!!"
}设置字段使用自定义分词器
PUT /my_index/_mapping/
{
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "my_analyzer"
}
}
}type底层结构及弃用原因
type是什么
type,是一个index中用来区分类似的数据的,类似的数据,但是可能有不同的fields,而且有不同的属性来控制索引建立、分词器. field的value,在底层的lucene中建立索引的时候,全部是opaque bytes类型,不区分类型的。 lucene是没有type的概念的,在document中,实际上将type作为一个document的field来存储,即type,es通过type来进行type的过滤和筛选。
es中不同type存储机制
一个index中的多个type,实际上是放在一起存储的,因此一个index下,不能有多个type重名,而类型或者其他设置不同的,因为那样是无法处理的
{
"goods": {
"mappings": {
"electronic_goods": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string",
},
"price": {
"type": "double"
},
"service_period": {
"type": "string"
}
}
},
"fresh_goods": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string",
},
"price": {
"type": "double"
},
"eat_period": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}
}
}
PUT /goods/electronic_goods/1
{
"name": "小米空调",
"price": 1999.0,
"service_period": "one year"
}
PUT /goods/fresh_goods/1
{
"name": "澳洲龙虾",
"price": 199.0,
"eat_period": "one week"
}es文档在底层的存储是这样子的
{
"goods": {
"mappings": {
"_type": {
"type": "string",
"index": "false"
},
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
"price": {
"type": "double"
}
"service_period": {
"type": "string"
},
"eat_period": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}底层数据存储格式
{
"_type": "electronic_goods",
"name": "小米空调",
"price": 1999.0,
"service_period": "one year",
"eat_period": ""
}
{
"_type": "fresh_goods",
"name": "澳洲龙虾",
"price": 199.0,
"service_period": "",
"eat_period": "one week"
}type弃用
同一索引下,不同type的数据存储其他type的field 大量空值,造成资源浪费。
所以,不同类型数据,要放到不同的索引中。
es9中,将会彻底删除type。
定制dynamic mapping
定制dynamic策略
true:遇到陌生字段,就进行dynamic mapping
false:新检测到的字段将被忽略。这些字段将不会被索引,因此将无法搜索,但仍将出现在返回点击的源字段中。这些字段不会添加到映射中,必须显式添加新字段。
strict:遇到陌生字段,就报错
创建mapping
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": "true"
}
}
}
}插入数据
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "my article",
"content": "this is my article",
"address": {
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
}
}报错
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason": "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [content] within [_doc] is not allowed"
}
],
"type": "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason": "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [content] within [_doc] is not allowed"
},
"status": 400
}自定义 dynamic mapping策略
es会根据传入的值,推断类型。
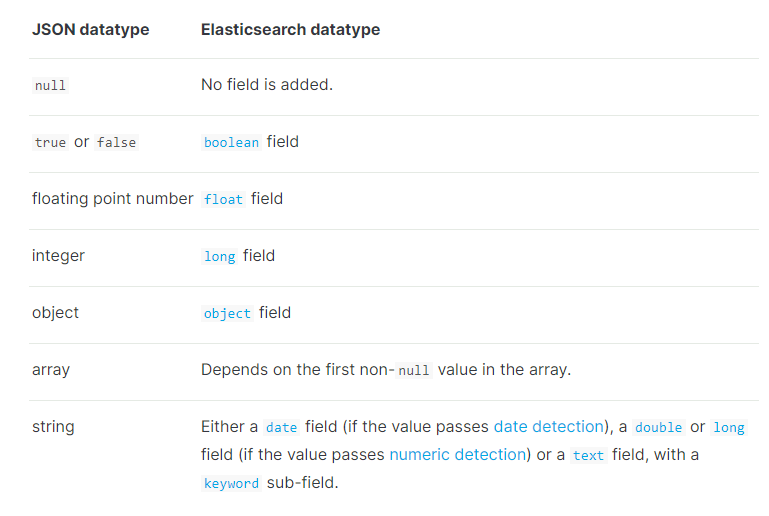
date_detection 日期探测
默认会按照一定格式识别date,比如yyyy-MM-dd。但是如果某个field先过来一个2017-01-01的值,就会被自动dynamic mapping成date,后面如果再来一个"hello world"之类的值,就会报错。可以手动关闭某个type的date_detection,如果有需要,自己手动指定某个field为date类型。
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"date_detection": false,
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": "true"
}
}
}
}测试
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "my article",
"content": "this is my article",
"address": {
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
},
"post_date":"2019-09-10"
}查看映射
GET /my_index/_mapping自定义日期格式
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_date_formats": ["MM/dd/yyyy"]
}
}插入数据
PUT my_index/_doc/1
{
"create_date": "09/25/2019"
}numeric_detection 数字探测
虽然json支持本机浮点和整数数据类型,但某些应用程序或语言有时可能将数字呈现为字符串。通常正确的解决方案是显式地映射这些字段,但是可以启用数字检测(默认情况下禁用)来自动完成这些操作。
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"numeric_detection": true
}
}
PUT my_index/_doc/1
{
"my_float": "1.0",
"my_integer": "1"
}定制自己的dynamic mapping template
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"en": {
"match": "*_en",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
]
}
}插入数据
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "this is my first article"
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/2
{
"title_en": "this is my first article"
}搜索
GET my_index/_search?q=first
GET my_index/_search?q=istitle没有匹配到任何的dynamic模板,默认就是standard分词器,不会过滤停用词,is会进入倒排索引,用is来搜索是可以搜索到的
title_en匹配到了dynamic模板,就是english分词器,会过滤停用词,is这种停用词就会被过滤掉,用is来搜索就搜索不到了
模板写法
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"integers": {
"match_mapping_type": "long",
"mapping": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
},
{
"strings": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"raw": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
}模板参数
"match": "long_*",
"unmatch": "*_text",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"path_match": "name.*",
"path_unmatch": "*.middle",
"match_pattern": "regex",
"match": "^profit_\d+$"场景
结构化搜索
默认情况下,elasticsearch将字符串字段映射为带有子关键字字段的文本字段。但是,如果只对结构化内容进行索引,而对全文搜索不感兴趣,则可以仅将“字段”映射为“关键字”。请注意,这意味着为了搜索这些字段,必须搜索索引所用的完全相同的值。
{
"strings_as_keywords": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}仅搜索
与前面的示例相反,如果您只关心字符串字段的全文搜索,并且不打算对字符串字段运行聚合、排序或精确搜索,您可以告诉弹性搜索将其仅映射为文本字段(这是5之前的默认行为)
{
"strings_as_text": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}norms 不关心评分
norms是指标时间的评分因素。如果您不关心评分,例如,如果您从不按评分对文档进行排序,则可以在索引中禁用这些评分因子的存储并节省一些空间。
{
"strings_as_keywords": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"norms": false,
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}零停机重建索引
零停机重建索引
场景:
一个field的设置是不能被修改的,如果要修改一个Field,那么应该重新按照新的mapping,建立一个index,然后将数据批量查询出来,重新用bulk api写入index中。
批量查询的时候,建议采用scroll api,并且采用多线程并发的方式来reindex数据,每次scoll就查询指定日期的一段数据,交给一个线程即可。
(1)一开始,依靠dynamic mapping,插入数据,但是不小心有些数据是2019-09-10这种日期格式的,所以title这种field被自动映射为了date类型,实际上它应该是string类型的
PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "2019-09-10"
}
PUT /my_index/_doc/2
{
"title": "2019-09-11"
}(2)当后期向索引中加入string类型的title值的时候,就会报错
PUT /my_index/_doc/3
{
"title": "my first article"
}报错
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason": "failed to parse [title]"
}
],
"type": "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason": "failed to parse [title]",
"caused_by": {
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "Invalid format: \"my first article\""
}
},
"status": 400
}(3)如果此时想修改title的类型,是不可能的
PUT /my_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}报错
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "mapper [title] of different type, current_type [date], merged_type [text]"
}
],
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "mapper [title] of different type, current_type [date], merged_type [text]"
},
"status": 400
}(4)此时,唯一的办法,就是进行reindex,也就是说,重新建立一个索引,将旧索引的数据查询出来,再导入新索引。
(5)如果说旧索引的名字,是old_index,新索引的名字是new_index,终端java应用,已经在使用old_index在操作了,难道还要去停止java应用,修改使用的index为new_index,才重新启动java应用吗?这个过程中,就会导致java应用停机,可用性降低。
(6)所以说,给java应用一个别名,这个别名是指向旧索引的,java应用先用着,java应用先用prod_index alias来操作,此时实际指向的是旧的my_index
PUT /my_index/_alias/prod_index(7)新建一个index,调整其title的类型为string
PUT /my_index_new
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}(8)使用scroll api将数据批量查询出来
GET /my_index/_search?scroll=1m
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 1
}返回
{
"_scroll_id": "DnF1ZXJ5VGhlbkZldGNoBQAAAAAAADpAFjRvbnNUWVZaVGpHdklqOV9zcFd6MncAAAAAAAA6QRY0b25zVFlWWlRqR3ZJajlfc3BXejJ3AAAAAAAAOkIWNG9uc1RZVlpUakd2SWo5X3NwV3oydwAAAAAAADpDFjRvbnNUWVZaVGpHdklqOV9zcFd6MncAAAAAAAA6RBY0b25zVFlWWlRqR3ZJajlfc3BXejJ3",
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": null,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_type": "my_type",
"_id": "1",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"title": "2019-01-02"
},
"sort": [
0
]
}
]
}
}(9)采用bulk api将scoll查出来的一批数据,批量写入新索引
POST /_bulk
{ "index": { "_index": "my_index_new", "_id": "1" }}
{ "title": "2019-09-10" }(10)反复循环8~9,查询一批又一批的数据出来,采取bulk api将每一批数据批量写入新索引
(11)将prod_index alias切换到my_index_new上去,java应用会直接通过index别名使用新的索引中的数据,java应用程序不需要停机,零提交,高可用
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{ "remove": { "index": "my_index", "alias": "prod_index" }},
{ "add": { "index": "my_index_new", "alias": "prod_index" }}
]
}(12)直接通过prod_index别名来查询,是否ok
GET /prod_index/_search生产实践:基于alias对client透明切换index
PUT /my_index_v1/_alias/my_indexclient对my_index进行操作
reindex操作,完成之后,切换v1到v2
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{ "remove": { "index": "my_index_v1", "alias": "my_index" }},
{ "add": { "index": "my_index_v2", "alias": "my_index" }}
]
}