singleton
默认情况下,Spring的IoC容器创建的Bean对象是单例的。来测试一下:
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className SpringBean
* @since 1.0
**/
public class SpringBean {
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="sb" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.SpringBean" />
</beans>@Test
public void testScope(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-scope.xml");
SpringBean sb1 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb1);
SpringBean sb2 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb2);
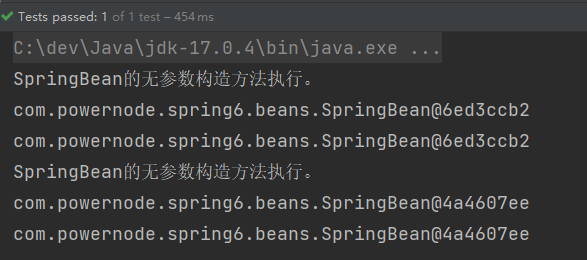
}执行结果:
通过测试得知:Spring的IoC容器中,默认情况下,Bean对象是单例的。
这个对象在什么时候创建的呢?可以为SpringBean提供一个无参数构造方法,测试一下,如下:
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className SpringBean
* @since 1.0
**/
public class SpringBean {
public SpringBean() {
System.out.println("SpringBean的无参数构造方法执行。");
}
}将测试程序中getBean()所在行代码注释掉:
@Test
public void testScope(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-scope.xml");
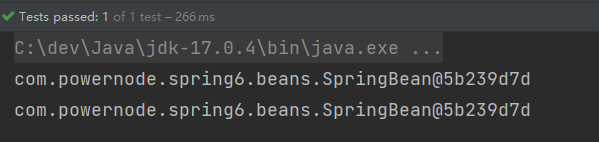
}执行测试程序:
通过测试得知,默认情况下,Bean对象的创建是在初始化Spring上下文的时候就完成的。
prototype
如果想让Spring的Bean对象以多例的形式存在,可以在bean标签中指定scope属性的值为:prototype,这样Spring会在每一次执行getBean()方法的时候创建Bean对象,调用几次则创建几次。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="sb" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.SpringBean" scope="prototype" />
</beans>@Test
public void testScope(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-scope.xml");
SpringBean sb1 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb1);
SpringBean sb2 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb2);
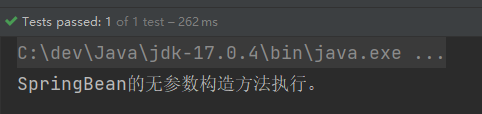
}执行结果:
我们可以把测试代码中的getBean()方法所在行代码注释掉:
@Test
public void testScope(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-scope.xml");
}执行结果:
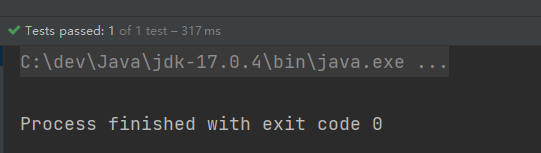
可以看到这一次在初始化Spring上下文的时候,并没有创建Bean对象。
那你可能会问:scope如果没有配置,它的默认值是什么呢?默认值是singleton,单例的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="sb" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.SpringBean" scope="singleton" />
</beans>@Test
public void testScope(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-scope.xml");
SpringBean sb1 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb1);
SpringBean sb2 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb2);
}执行结果:
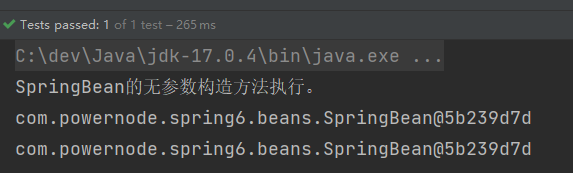
通过测试得知,没有指定scope属性时,默认是singleton单例的。
其它scope
scope属性的值不止两个,它一共包括8个选项:
singleton:默认的,单例。
prototype:原型。每调用一次getBean()方法则获取一个新的Bean对象。或每次注入的时候都是新对象。
request:一个请求对应一个Bean。仅限于在WEB应用中使用。
session:一个会话对应一个Bean。仅限于在WEB应用中使用。
global session:portlet应用中专用的。如果在Servlet的WEB应用中使用global session的话,和session一个效果。(portlet和servlet都是规范。servlet运行在servlet容器中,例如Tomcat。portlet运行在portlet容器中。)
application:一个应用对应一个Bean。仅限于在WEB应用中使用。
websocket:一个websocket生命周期对应一个Bean。仅限于在WEB应用中使用。
自定义scope:很少使用。
接下来咱们自定义一个Scope,线程级别的Scope,在同一个线程中,获取的Bean都是同一个。跨线程则是不同的对象:(以下内容作为了解)
第一步:自定义Scope。(实现Scope接口)
spring内置了线程范围的类:org.springframework.context.support.SimpleThreadScope,可以直接用。
第二步:将自定义的Scope注册到Spring容器中。
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomScopeConfigurer">
<property name="scopes">
<map>
<entry key="myThread">
<bean class="org.springframework.context.support.SimpleThreadScope"/>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>第三步:使用Scope。
<bean id="sb" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.SpringBean" scope="myThread" />编写测试程序:
@Test
public void testCustomScope(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-scope.xml");
SpringBean sb1 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
SpringBean sb2 = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb1);
System.out.println(sb2);
// 启动线程
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SpringBean a = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
SpringBean b = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}).start();
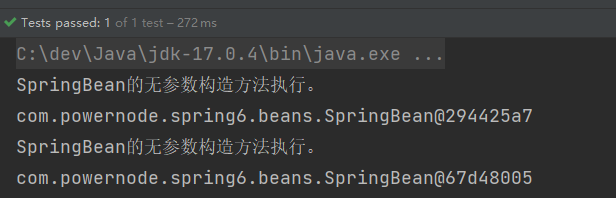
}执行结果: