默认自带字段解析
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"_seq_no" : 10,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "Bootstrap开发教程1",
"description" : "Bootstrap是由Twitter推出的一个前台页面开发css框架,是一个非常流行的开发框架,此框架集成了多种页面效果。此开发框架包含了大量的CSS、JS程序代码,可以帮助开发者(尤其是不擅长css页面开发的程序人员)轻松的实现一个css,不受浏览器限制的精美界面css效果。",
"studymodel" : "201002",
"price" : 38.6,
"timestamp" : "2019-08-25 19:11:35",
"pic" : "group1/M00/00/00/wKhlQFs6RCeAY0pHAAJx5ZjNDEM428.jpg",
"tags" : [
"bootstrap",
"开发"
]
}
}_index
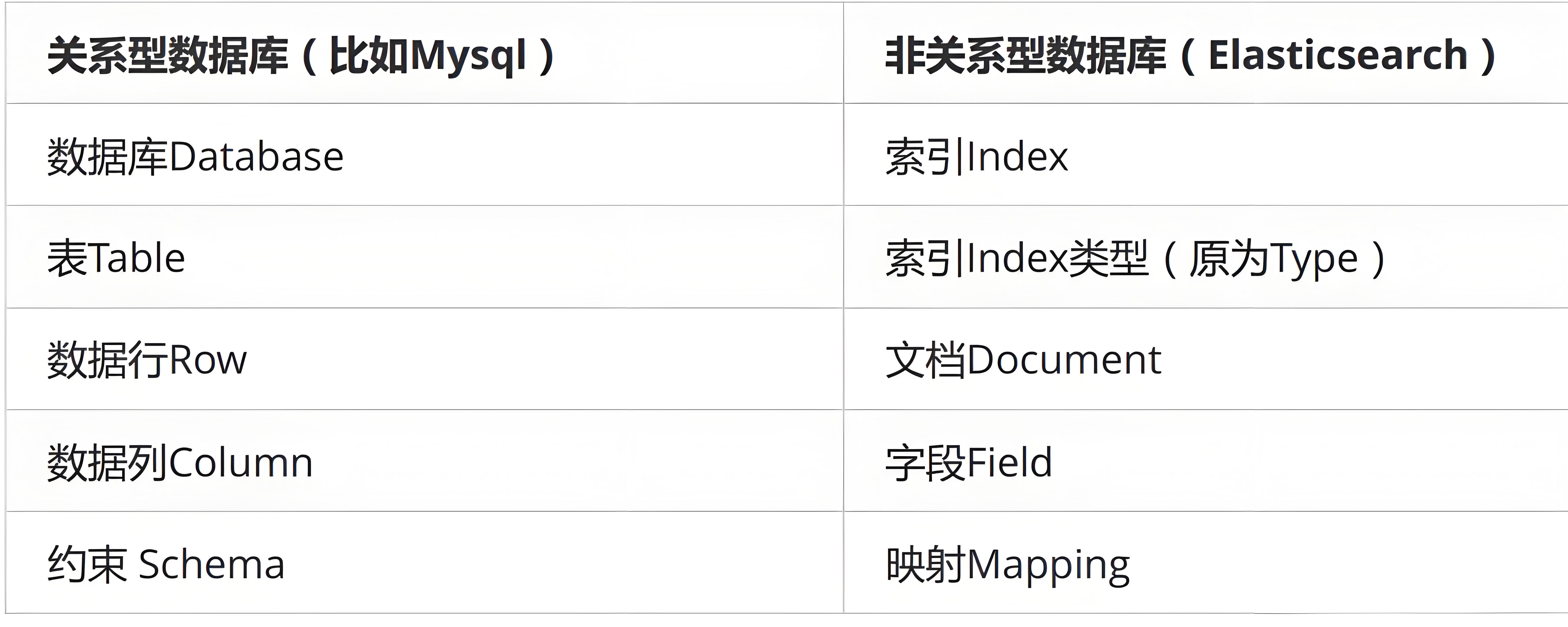
含义:此文档属于哪个索引
原则:类似数据放在一个索引中。数据库中表的定义规则。如图书信息放在book索引中,员工信息放在employee索引中。各个索引存储和搜索时互不影响。
定义规则:英文小写。尽量不要使用特殊字符。order user
_type
含义:类别。book java node
注意:以后的es9将彻底删除此字段,所以当前版本在不断弱化type。不需要关注。见到_type都为doc。
_id
含义:文档的唯一标识。就像表的id主键。结合索引可以标识和定义一个文档。
生成:手动(put /index/_doc/id)、自动
创建索引时,不同数据放到不同索引中
生成文档id
手动生成id
场景:数据从其他系统导入时,本身有唯一主键。如数据库中的图书、员工信息等。
用法:put /index/_doc/id
PUT /test_index/_doc/1
{
"test_field": "test"
}自动生成id
用法:POST /index/_doc
POST /test_index/_doc
{
"test_field": "test1"
}返回:
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "x29LOm0BPsY0gSJFYZAl",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}自动id特点:
长度为20个字符,URL安全,base64编码,GUID,分布式生成不冲突
_source 字段
_source
含义:插入数据时的所有字段和值。在get获取数据时,在_source字段中原样返回。
GET /book/_doc/1
定制返回字段
就像sql不要select *,而要select name,price from book …一样。
GET /book/_doc/1?__source_includes=name,price
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"_seq_no" : 10,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"price" : 38.6,
"name" : "Bootstrap开发教程1"
}
}文档的替换与删除
全量替换
执行两次,返回结果中版本号(_version)在不断上升。此过程为全量替换。
PUT /test_index/_doc/1
{
"test_field": "test"
}实质:旧文档的内容不会立即删除,只是标记为deleted。适当的时机,集群会将这些文档删除。
强制创建
为防止覆盖原有数据,我们在新增时,设置为强制创建,不会覆盖原有文档。
语法:PUT /index/ *doc/id/*create
PUT /test_index/_doc/1/_create
{
"test_field": "test"
}返回
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[2]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [1])",
"index_uuid": "lqzVqxZLQuCnd6LYtZsMkg",
"shard": "0",
"index": "test_index"
}
],
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[2]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [1])",
"index_uuid": "lqzVqxZLQuCnd6LYtZsMkg",
"shard": "0",
"index": "test_index"
},
"status": 409
}删除
DELETE /index/_doc/id
DELETE /test_index/_doc/1/实质:旧文档的内容不会立即删除,只是标记为deleted。适当的时机,集群会将这些文档删除。
lazy delete
局部替换 partial update
使用 PUT /index/type/id 为文档全量替换,需要将文档所有数据提交。
partial update局部替换则只修改变动字段。
用法:
post /index/type/id/_update
{
"doc": {
"field":"value"
}
}图解内部原理
内部与全量替换是一样的,旧文档标记为删除,新建一个文档。
优点:
大大减少网络传输次数和流量,提升性能
减少并发冲突发生的概率。
演示
插入文档
PUT /test_index/_doc/5
{
"test_field1": "itcst",
"test_field2": "itheima"
}修改字段1
POST /test_index/_doc/5/_update
{
"doc": {
"test_field2": " itheima 2"
}
}使用脚本更新
es可以内置脚本执行复杂操作。例如painless脚本。
注意:groovy脚本在es6以后就不支持了。原因是耗内存,不安全远程注入漏洞。
内置脚本
需求1:修改文档6的num字段,+1。
插入数据
PUT /test_index/_doc/6
{
"num": 0,
"tags": []
}执行脚本操作
POST /test_index/_doc/6/_update
{
"script" : "ctx._source.num+=1"
}查询数据
GET /test_index/_doc/6返回
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "6",
"_version" : 2,
"_seq_no" : 23,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"num" : 1,
"tags" : [ ]
}
}需求2:搜索所有文档,将num字段乘以2输出
插入数据
PUT /test_index/_doc/7
{
"num": 5
}查询
GET /test_index/_search
{
"script_fields": {
"my_doubled_field": {
"script": {
"lang": "expression",
"source": "doc['num'] * multiplier",
"params": {
"multiplier": 2
}
}
}
}
}返回
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "7",
"_score" : 1.0,
"fields" : {
"my_doubled_field" : [
10.0
]
}
}外部脚本
Painless是内置支持的。脚本内容可以通过多种途径传给 es,包括 rest 接口,或者放到 config/scripts目录等,默认开启。
注意:脚本性能低下,且容易发生注入,本教程忽略。
官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-scripting-using.html
图解es的并发问题
如同秒杀,多线程情况下,es同样会出现并发冲突问题。
图解悲观锁与乐观锁机制
为控制并发问题,我们通常采用锁机制。分为悲观锁和乐观锁两种机制。
悲观锁:很悲观,所有情况都上锁。此时只有一个线程可以操作数据。具体例子为数据库中的行级锁、表级锁、读锁、写锁等。
特点:优点是方便,直接加锁,对程序透明。缺点是效率低。
乐观锁:很乐观,对数据本身不加锁。提交数据时,通过一种机制验证是否存在冲突,如es中通过版本号验证。
特点:优点是并发能力高。缺点是操作繁琐,在提交数据时,可能反复重试多次。
图解es内部基于_version乐观锁控制
实验基于_version的版本控制
es对于文档的增删改都是基于版本号。
1新增多次文档:
PUT /test_index/_doc/3
{
"test_field": "test"
}返回版本号递增
2删除此文档
DELETE /test_index/_doc/3返回
DELETE /test_index/_doc/3
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 6,
"result" : "deleted",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 7,
"_primary_term" : 1
}3再新增
PUT /test_index/_doc/3
{
"test_field": "test"
}可以看到版本号依然递增,验证延迟删除策略。
如果删除一条数据立马删除的话,所有分片和副本都要立马删除,对es集群压力太大。
图解es内部并发控制
es内部主从同步时,是多线程异步。乐观锁机制。
演示客户端程序基于_version并发操作流程
java python客户端更新的机制。
新建文档
PUT /test_index/_doc/5
{
"test_field": "itcast"
}返回:
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 8,
"_primary_term" : 1
}客户端1修改。带版本号1。
首先获取数据的当前版本号
GET /test_index/_doc/5更新文档
PUT /test_index/_doc/5?version=1
{
"test_field": "itcast1"
}
PUT /test_index/_doc/5?if_seq_no=21&if_primary_term=1
{
"test_field": "itcast1"
}客户端2并发修改。带版本号1。
PUT /test_index/_doc/5?version=1
{
"test_field": "itcast2"
}
PUT /test_index/_doc/5?if_seq_no=21&if_primary_term=1
{
"test_field": "itcast1"
}报错。
客户端2重新查询。得到最新版本为2。seq_no=22
GET /test_index/_doc/4客户端2并发修改。带版本号2。
PUT /test_index/_doc/4?version=2
{
"test_field": "itcast2"
}
es7
PUT /test_index/_doc/5?if_seq_no=22&if_primary_term=1
{
"test_field": "itcast2"
}修改成功。
演示自己手动控制版本号 external version
背景:已有数据是在数据库中,有自己手动维护的版本号的情况下,可以使用external version控制。hbase。
要求:修改时external version要大于当前文档的_version
对比:基于_version时,修改的文档version等于当前文档的版本号。
使用?version=1&version_type=external
新建文档
PUT /test_index/_doc/4
{
"test_field": "itcast"
}更新文档:
客户端1修改文档
PUT /test_index/_doc/4?version=2&version_type=external
{
"test_field": "itcast1"
}客户端2同时修改
PUT /test_index/_doc/4?version=2&version_type=external
{
"test_field": "itcast2"
}返回:
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[4]: version conflict, current version [2] is higher or equal to the one provided [2]",
"index_uuid": "-rqYZ2EcSPqL6pu8Gi35jw",
"shard": "1",
"index": "test_index"
}
],
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[4]: version conflict, current version [2] is higher or equal to the one provided [2]",
"index_uuid": "-rqYZ2EcSPqL6pu8Gi35jw",
"shard": "1",
"index": "test_index"
},
"status": 409
}客户端2重新查询数据
GET /test_index/_doc/4客户端2重新修改数据
PUT /test_index/_doc/4?version=3&version_type=external
{
"test_field": "itcast2"
}更新时 retry_on_conflict 参数
retry_on_conflict
指定重试次数
POST /test_index/_doc/5/_update?retry_on_conflict=3
{
"doc": {
"test_field": "itcast1"
}
}与 _version结合使用
POST /test_index/_doc/5/_update?retry_on_conflict=3&version=22&version_type=external
{
"doc": {
"test_field": "itcast1"
}
}批量查询 mget
单条查询 GET /test_index/_doc/1,如果查询多个id的文档一条一条查询,网络开销太大。
mget 批量查询:
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : 1
},
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : 7
}
]
}返回:
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 6,
"_seq_no" : 12,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"test_field" : "test12333123321321"
}
},
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_version" : 6,
"_seq_no" : 18,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"test_field" : "test3213"
}
}
]
}提示去掉type
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_id" : 2
},
{
"_index" : "test_index",
"_id" : 3
}
]
}同一索引下批量查询:
GET /test_index/_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_id" : 2
},
{
"_id" : 3
}
]
}第三种写法:搜索写法
post /test_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"ids" : {
"values" : ["1", "7"]
}
}
}批量增删改 bulk
Bulk 操作解释将文档的增删改查一些列操作,通过一次请求全都做完。减少网络传输次数。
语法:
POST /_bulk
{"action": {"metadata"}}
{"data"}如下操作,删除5,新增14,修改2。
POST /_bulk
{ "delete": { "_index": "test_index", "_id": "5" }}
{ "create": { "_index": "test_index", "_id": "14" }}
{ "test_field": "test14" }
{ "update": { "_index": "test_index", "_id": "2"} }
{ "doc" : {"test_field" : "bulk test"} }总结:
1功能:
delete:删除一个文档,只要1个json串就可以了
create:相当于强制创建 PUT /index/type/id/_create
index:普通的put操作,可以是创建文档,也可以是全量替换文档
update:执行的是局部更新partial update操作
2格式:每个json不能换行。相邻json必须换行。
3隔离:每个操作互不影响。操作失败的行会返回其失败信息。
4实际用法:bulk请求一次不要太大,否则一下积压到内存中,性能会下降。所以,一次请求几千个操作、大小在几M正好。
文档概念学习总结
章节回顾
1文档的增删改查
2文档字段解析
3内部锁机制
4批量查询修改
es是什么
一个分布式的文档数据存储系统distributed document store。es看做一个分布式nosql数据库。如redis\mongoDB\hbase。
文档数据:es可以存储和操作json文档类型的数据,而且这也是es的核心数据结构。 存储系统:es可以对json文档类型的数据进行存储,查询,创建,更新,删除,等等操作。
应用场景
大数据。es的分布式特点,水平扩容承载大数据。
数据结构灵活。列随时变化。使用关系型数据库将会建立大量的关联表,增加系统复杂度。
数据操作简单。就是查询,不涉及事务。
举例
电商页面、传统论坛页面等。面向的对象比较复杂,但是作为终端,没有太复杂的功能(事务),只涉及简单的增删改查crud。
这个时候选用ES这种NoSQL型的数据存储,比传统的复杂的事务强大的关系型数据库,更加合适一些。无论是性能,还是吞吐量,可能都会更好。
