什么是mapping映射
概念:自动或手动为index中的_doc建立的一种数据结构和相关配置,简称为mapping映射。
插入几条数据,让es自动为我们建立一个索引
PUT /website/_doc/1
{
"post_date": "2019-01-01",
"title": "my first article",
"content": "this is my first article in this website",
"author_id": 11400
}
PUT /website/_doc/2
{
"post_date": "2019-01-02",
"title": "my second article",
"content": "this is my second article in this website",
"author_id": 11400
}
PUT /website/_doc/3
{
"post_date": "2019-01-03",
"title": "my third article",
"content": "this is my third article in this website",
"author_id": 11400
}对比数据库建表语句
create table website(
post_date date,
title varchar(50),
content varchar(100),
author_id int(11)
);动态映射:dynamic mapping,自动为我们建立index,以及对应的mapping,mapping中包含了每个field对应的数据类型,以及如何分词等设置。
重点:我们当然,后面会讲解,也可以手动在创建数据之前,先创建index,以及对应的mapping
GET /website/_mapping/
{
"website" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"author_id" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"content" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"post_date" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"title" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}尝试各种搜索
GET /website/_search?q=2019 0条结果
GET /website/_search?q=2019-01-01 1条结果
GET /website/_search?q=post_date:2019-01-01 1条结果
GET /website/_search?q=post_date:2019 0 条结果搜索结果为什么不一致,因为es自动建立mapping的时候,设置了不同的field不同的data type。不同的data type的分词、搜索等行为是不一样的。所以出现了_all field和post_date field的搜索表现完全不一样。
精确匹配与全文搜索的对比分析
exact value 精确匹配
2019-01-01,exact value,搜索的时候,必须输入2019-01-01,才能搜索出来
如果你输入一个01,是搜索不出来的
select * from book where name= 'java'
full text 全文检索
搜“笔记电脑”,笔记本电脑词条会不会出现。
select * from book where name like '%java%'
(1)缩写 vs. 全称:cn vs. china
(2)格式转化:like liked likes
(3)大小写:Tom vs tom
(4)同义词:like vs love
2019-01-01,2019 01 01,搜索2019,或者01,都可以搜索出来
china,搜索cn,也可以将china搜索出来
likes,搜索like,也可以将likes搜索出来
Tom,搜索tom,也可以将Tom搜索出来
like,搜索love,同义词,也可以将like搜索出来
就不是说单纯的只是匹配完整的一个值,而是可以对值进行拆分词语后(分词)进行匹配,也可以通过缩写、时态、大小写、同义词等进行匹配。深入 NPL,自然语义处理。
全文检索下倒排索引核心原理快速揭秘
doc1:I really liked my small dogs, and I think my mom also liked them.
doc2:He never liked any dogs, so I hope that my mom will not expect me to liked him.
分词,初步的倒排索引的建立
term |
doc1 |
doc2 |
|---|---|---|
I |
* |
* |
really |
* |
|
liked |
* |
* |
my |
* |
* |
small |
* |
|
dogs |
* |
|
and |
* |
|
think |
* |
|
mom |
* |
* |
also |
* |
|
them |
* |
|
He |
* |
|
never |
* |
|
any |
* |
|
so |
* |
|
hope |
* |
|
that |
* |
|
will |
* |
|
not |
* |
|
expect |
* |
|
me |
* |
|
to |
* |
|
him |
* |
演示了一下倒排索引最简单的建立的一个过程
搜索
mother like little dog,不可能有任何结果
mother
like
little
dog
这不是我们想要的结果。同义词mom\mother在我们人类看来是一样。想进行标准化操作。
重建倒排索引
normalization正规化,建立倒排索引的时候,会执行一个操作,也就是说对拆分出的各个单词进行相应的处理,以提升后面搜索的时候能够搜索到相关联的文档的概率
时态的转换,单复数的转换,同义词的转换,大小写的转换
mom ―> mother
liked ―> like
small ―> little
dogs ―> dog
重新建立倒排索引,加入normalization,再次用mother liked little dog搜索,就可以搜索到了
word |
doc1 |
doc2 |
normalization |
|---|---|---|---|
I |
* |
* |
|
really |
* |
||
like |
* |
* |
liked ―> like |
my |
* |
* |
|
little |
* |
small ―> little |
|
dog |
* |
dogs ―> dog |
|
and |
* |
||
think |
* |
||
mother |
* |
* |
mom ―> mother |
also |
* |
||
them |
* |
||
He |
* |
||
never |
* |
||
any |
* |
||
so |
* |
||
hope |
* |
||
that |
* |
||
will |
* |
||
not |
* |
||
expect |
* |
||
me |
* |
||
to |
* |
||
him |
* |
重新搜索
搜索:mother liked little dog,
对搜索条件经行分词 normalization
mother
liked -》like
little
dog
doc1和doc2都会搜索出来
分词器 analyzer
什么是分词器 analyzer
作用:切分词语,normalization(提升recall召回率)
给你一段句子,然后将这段句子拆分成一个一个的单个的单词,同时对每个单词进行normalization(时态转换,单复数转换)
recall,召回率:搜索的时候,增加能够搜索到的结果的数量
analyzer 组成部分:
1、character filter:在一段文本进行分词之前,先进行预处理,比如说最常见的就是,过滤html标签(hello --> hello),& --> and(I&you --> I and you)
2、tokenizer:分词,hello you and me --> hello, you, and, me
3、token filter:lowercase,stop word,synonymom,dogs --> dog,liked --> like,Tom --> tom,a/the/an --> 干掉,mother --> mom,small --> little
stop word 停用词: 了 的 呢。
一个分词器,很重要,将一段文本进行各种处理,最后处理好的结果才会拿去建立倒排索引。
内置分词器的介绍
例句:Set the shape to semi-transparent by calling set_trans(5)
standard analyzer标准分词器:set, the, shape, to, semi, transparent, by, calling, set_trans, 5(默认的是standard)
simple analyzer简单分词器:set, the, shape, to, semi, transparent, by, calling, set, trans
whitespace analyzer:Set, the, shape, to, semi-transparent, by, calling, set_trans(5)
language analyzer(特定的语言的分词器,比如说,english,英语分词器):set, shape, semi, transpar, call, set_tran, 5
官方文档:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.4/analysis-analyzers.html

query string根据字段分词策略
query string分词
query string必须以和index建立时相同的analyzer进行分词
query string对exact value和full text的区别对待
如: date:exact value 精确匹配
text: full text 全文检索
测试分词器
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "Text to analyze 80"
}返回值:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "text",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "analyze",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "80",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "<NUM>",
"position" : 3
}
]
}token 实际存储的term 关键字
position 在此词条在原文本中的位置
start_offset/end_offset字符在原始字符串中的位置
mapping回顾总结
(1)往es里面直接插入数据,es会自动建立索引,同时建立对应的mapping。(dynamic mapping)
(2)mapping中就自动定义了每个field的数据类型
(3)不同的数据类型(比如说text和date),可能有的是exact value,有的是full text
(4)exact value,在建立倒排索引的时候,分词的时候,是将整个值一起作为一个关键词建立到倒排索引中的;full text,会经历各种各样的处理,分词,normaliztion(时态转换,同义词转换,大小写转换),才会建立到倒排索引中。
(5)同时呢,exact value和full text类型的field就决定了,在一个搜索过来的时候,对exact value field或者是full text field进行搜索的行为也是不一样的,会跟建立倒排索引的行为保持一致;比如说exact value搜索的时候,就是直接按照整个值进行匹配,full text query string,也会进行分词和normalization再去倒排索引中去搜索
(6)可以用es的dynamic mapping,让其自动建立mapping,包括自动设置数据类型;也可以提前手动创建index和tmapping,自己对各个field进行设置,包括数据类型,包括索引行为,包括分词器,等。
mapping的核心数据类型以及dynamic mapping
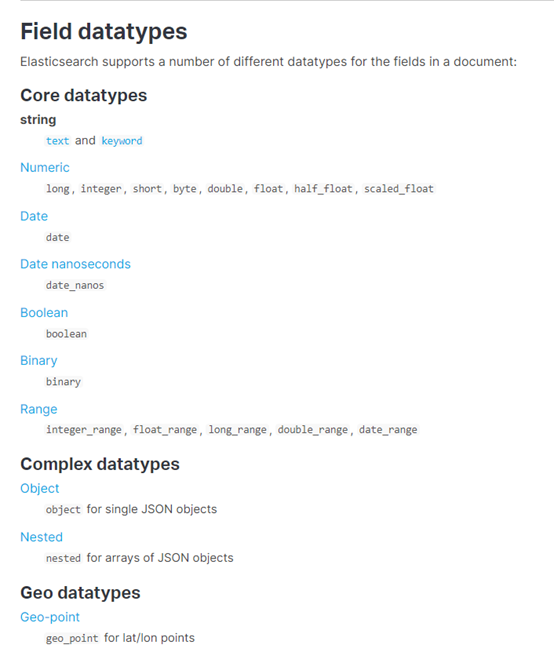
核心的数据类型
string :text and keyword
byte,short,integer,long,float,double
boolean
date
详见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.3/mapping-types.html
下图是ES7.3核心的字段类型如下:
dynamic mapping 推测规则
true or false --> boolean
123 --> long
123.45 --> double
2019-01-01 --> date
"hello world" --> text/keywod
查看mapping
GET /index/_mapping/
手动管理mapping
查询所有索引的映射
GET /_mapping
创建映射 !!
创建索引后,应该立即手动创建映射
PUT book/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"description": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer":"english",
"search_analyzer":"english"
},
"pic":{
"type":"text",
"index":false
},
"studymodel":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}Text 文本类型
1)analyzer
通过analyzer属性指定分词器。
上边指定了analyzer是指在索引和搜索都使用english,如果单独想定义搜索时使用的分词器则可以通过search_analyzer属性。
2)index
index属性指定是否索引。
默认为index=true,即要进行索引,只有进行索引才可以从索引库搜索到。
但是也有一些内容不需要索引,比如:商品图片地址只被用来展示图片,不进行搜索图片,此时可以将index设置为false。
删除索引,重新创建映射,将pic的index设置为false,尝试根据pic去搜索,结果搜索不到数据。
3)store
是否在source之外存储,每个文档索引后会在 ES中保存一份原始文档,存放在"source"中,一般情况下不需要设置store为true,因为在source中已经有一份原始文档了。
测试
PUT book/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"description": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer":"english",
"search_analyzer":"english"
},
"pic":{
"type":"text",
"index":false
},
"studymodel":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}插入文档:
PUT /book/_doc/1
{
"name":"Bootstrap开发框架",
"description":"Bootstrap是由Twitter推出的一个前台页面开发框架,在行业之中使用较为广泛。此开发框架包含了大量的CSS、JS程序代码,可以帮助开发者(尤其是不擅长页面开发的程序人员)轻松的实现一个不受浏览器限制的精美界面效果。",
"pic":"group1/M00/00/01/wKhlQFqO4MmAOP53AAAcwDwm6SU490.jpg",
"studymodel":"201002"
}Get /book/_search?q=name:开发
Get /book/_search?q=description:开发
Get /book/_search?q=pic:group1/M00/00/01/wKhlQFqO4MmAOP53AAAcwDwm6SU490.jpg
Get /book/_search?q=studymodel:201002
通过测试发现:name和description都支持全文检索,pic不可作为查询条件。
keyword关键字字段
目前已经取代了"index": false。上边介绍的text文本字段在映射时要设置分词器,keyword字段为关键字字段,通常搜索keyword是按照整体搜索,所以创建keyword字段的索引时是不进行分词的,比如:邮政编码、手机号码、身份证等。keyword字段通常用于过虑、排序、聚合等。
date日期类型
日期类型不用设置分词器。
通常日期类型的字段用于排序。
format
通过format设置日期格式
例子:
下边的设置允许date字段存储年月日时分秒、年月日及毫秒三种格式。
"properties": {
"timestamp": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd"
}
}插入文档:
Post book/doc/3
{
"name": "spring开发基础",
"description": "spring 在java领域非常流行,java程序员都在用。",
"studymodel": "201001",
"pic":"group1/M00/00/01/wKhlQFqO4MmAOP53AAAcwDwm6SU490.jpg",
"timestamp":"2018-07-04 18:28:58"
}数值类型
下边是ES支持的数值类型

1、尽量选择范围小的类型,提高搜索效率
2、对于浮点数尽量用比例因子,比如一个价格字段,单位为元,我们将比例因子设置为100这在ES中会按 分 存储,映射如下:
"price": {
"type": "scaled_float",
"scaling_factor": 100
},由于比例因子为100,如果我们输入的价格是23.45则ES中会将23.45乘以100存储在ES中。
如果输入的价格是23.456,ES会将23.456乘以100再取一个接近原始值的数,得出2346。
使用比例因子的好处是整型比浮点型更易压缩,节省磁盘空间。
如果比例因子不适合,则从下表选择范围小的去用:
更新已有映射,并插入文档:
PUT book/doc/3
{
"name": "spring开发基础",
"description": "spring 在java领域非常流行,java程序员都在用。",
"studymodel": "201001",
"pic":"group1/M00/00/01/wKhlQFqO4MmAOP53AAAcwDwm6SU490.jpg",
"timestamp":"2018-07-04 18:28:58",
"price":38.6
}修改映射
只能创建index时手动建立mapping,或者新增field mapping,但是不能update field mapping。
因为已有数据按照映射早已分词存储好。如果修改,那这些存量数据怎么办。
新增一个字段mapping
PUT /book/_mapping/
{
"properties" : {
"new_field" : {
"type" : "text",
"index": "false"
}
}
}如果修改mapping,会报错
PUT /book/_mapping/
{
"properties" : {
"studymodel" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
}返回:
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "mapper [studymodel] of different type, current_type [text], merged_type [keyword]"
}
],
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "mapper [studymodel] of different type, current_type [text], merged_type [keyword]"
},
"status": 400
}删除映射
通过删除索引来删除映射。
复杂数据类型
multivalue field
{ "tags": [ "tag1", "tag2" ]}
建立索引时与string是一样的,数据类型不能混
empty field
null,[],[null]
object field
PUT /company/_doc/1
{
"address": {
"country": "china",
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
},
"name": "jack",
"age": 27,
"join_date": "2019-01-01"
}address:object类型
查询映射
GET /company/_mapping
{
"company" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"address" : {
"properties" : {
"city" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"country" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"province" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
},
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"join_date" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}object
{
"address": {
"country": "china",
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
},
"name": "jack",
"age": 27,
"join_date": "2017-01-01"
}底层存储格式
{
"name": [jack],
"age": [27],
"join_date": [2017-01-01],
"address.country": [china],
"address.province": [guangdong],
"address.city": [guangzhou]
}对象数组:
{
"authors": [
{ "age": 26, "name": "Jack White"},
{ "age": 55, "name": "Tom Jones"},
{ "age": 39, "name": "Kitty Smith"}
]
}存储格式:
{
"authors.age": [26, 55, 39],
"authors.name": [jack, white, tom, jones, kitty, smith]
}