Angular介绍
Angular是谷歌开发的一款开源的web前端框架,诞生于2009年,由Misko Hevery 等人创建,后为Google所收购。是一款优秀的前端JS框架,已经被用于Google的多款产品当中。 根据项目数统计angular(1.x 、2.x 、4.x、5.x、6.x、7.x 、8.x、9.x)是现在网上使用量最大的框架。
Angular基于TypeScript,和react、vue相比Angular更适合中大型企业级项目。
Angular环境搭建
1、安装前准备工作:
1.1、安装nodejs 安装angular的计算机上面必须安装最新的nodejs--注意安装nodejs稳定版本
1.2、选择一个 命令工具, npm, cnpm, yarn ,任选其一
设置淘宝源镜像 ,如果你用npm
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org如果你用cnpm , 安装cnpm npm可能安装失败建议先用npm安装一下cnpm用淘宝镜像安装
https://npm.taobao.org/
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org或者 安装yarn ,注意,只要选 一个命令工具就行
yarn
npm install yarn -g然后切换为淘宝源你才能感受到速度:
yarn config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org --global``yarn config set disturl https://npm.taobao.org/dist --global好了,真的很简单,它的命令与npm几乎一样:
初始化:yarn init
安装一个包:yarn add 包名
更新一个包:yarn upgrade 包名
删除一个包:yarn remove 包名
安装所有包:yarn或者yarn install
安装Angular CLI
全局安装typescript(可选)
$ npm install -g typescript// 新建项目的时候会自动安装typescript(非全局)所以这里也可以不用安装。全局安装Angular CLI
yarn global add @angular/cli 或者 npm install @angular/cli -g如果要卸载,执行下面命令:
yarn global remove @angular/cli
经过不算漫长的等待,你的Angular CLI就装好了。确认一下:
检验安装是否成功 ng version 或者 ng v
新建Angular项目
新建Angular项目
ng new my-app
如果要跳过npm i安装 ng new my-app --skip-install
趁着它在下载,来看一下运行ng new之后Angular cli已经帮我们干了什么:
那么,这时候Angular cli帮你干了以下这么多事情:
创建 my-app 目录
应用程序相关的源文件和目录将会被创建
应用程序的所有依赖 (package.json中配置的依赖项) 将会被自动安装
自动配置项目中的 TypeScript 开发环境
自动配置 Karma 单元测试环境
自动配置 Protractor (end-to-end) 测试环境
创建 environment 相关的文件并初始化为默认的设置
启动项目
安装完成之后就可以启动项目了:
cd my-app //进入my-app
npm start 或者 ng serve //启服务
ng serve命令会启动开发服务器,监听文件变化,并在修改这些文件时重新构建此应用。 使用--open(或-o)参数可以自动打开浏览器并访问http://localhost:4200/。
ng serve命令提供了很多参数,可以适当参考。 以下参数仅供参考:
--dry-run: boolean, 默认为 false, 若设置 dry-run 则不会创建任何文件
--verbose: boolean, 默认为 false
--link-cli: boolean, 默认为 false, 自动链接到 @angular/cli 包
--skip-install: boolean, 默认为 false, 表示跳过 npm install
--skip-git: boolean, 默认为 false, 表示该目录不初始化为 git 仓库
--skip-tests: boolean, 默认为 false, 表示不创建 tests 相关文件
--skip-commit: boolean, 默认为 false, 表示不进行初始提交
--directory: string, 用于设置创建的目录名,默认与应用程序的同名
--source-dir: string, 默认为 'src', 用于设置源文件目录的名称
--stylring, 默认为 'css', 用于设置选用的样式语法 ('css', 'less' or 'scss')
--prefix: string, 默认为 'app', 用于设置创建新组件时,组件选择器使用的前缀
--mobile: boolean, 默认为 false,表示是否生成 Progressive Web App 应用程序
--routing: boolean, 默认为 false, 表示新增带有路由信息的模块,并添加到根模块中
--inline-style: boolean, 默认为 false, 表示当创建新的应用程序时,使用内联样式
--inline-template: boolean, 默认为 false, 表示当创建新的应用程序时,使用内联模板其他文件:
.editorconfig: 给你的编辑器看的一个简单配置文件
.gitignore: git 排除文件
angular.json: angular cli 的配置文件
package.json:npm 配置文件,项目使用到的第三方依赖包
protractor.conf.js- :运行 ng e2e 的时候会用到
README.md:项目的基础文档
tsconfig.json:TypeScript 编译器的配置
tslint.json:运行 ng lint 时会用到Angular CLI简单使用
新建组件
ng generate component newsinstalling component
create src/app/great-angular/news.component.css
create src/app/great-angular/news.component.html
create src/app/great-angular/news.component.spec.ts
create src/app/great-angular/news.component.ts
update src/app/app.module.ts
如你所见,Angular cli帮我们干了如下事情:
src/app/news 目录被创建
news目录下会生成以下四个文件:
CSS 样式文件,用于设置组件的样式
HTML 模板文件,用于设置组件的模板
TypeScript 文件,里面包含一个 组件类和组件的元信息
Spec 文件,包含组件相关的测试用例
news 组件会被自动地添加到 app.module.ts @NgModule 装饰器的 declarations 属性中。
其他命令
Angualr CLI提供了许多常用命令供我们选择:
ng generate class my-new-class // 新建类, 新建一个名为my-new-class的类 (class)
ng generate component my-new-component // 新建组件
ng generate directive my-new-directive // 新建指令
ng generate enum my-new-enum // 新建枚举
ng generate module my-new-module // 新建模块
ng generate pipe my-new-pipe // 新建管道
ng generate service my-new-service // 新建服务
当然选择。。简写:
ng g cl my-new-class // 新建 class
ng g c my-new-component // 新建组件
ng g d my-new-directive // 新建指令
ng g e my-new-enum // 新建枚举
ng g m my-new-module // 新建模块
ng g p my-new-pipe // 新建管道
ng g s my-new-service // 新建服务
单元测试
Angular默认帮我们集成了``karma`测试框架,我们只需要: ng test
端到端测试
ng e2e
构建应用程序
ng build
其中过程应该是这样的: Angular CLI 从 .angular-cli.json 文件中加载配置信息 Angular CLI 运行 Webpack 打包项目相关的 html、 CSS 等文件 打包后的资源,将被输出到配置文件中 outDir 所指定的目录,默认是输出到 dist 目录。
Angular开发工具介绍
Visual Studio Code
目录结构分析)Angular目录结构分析
app.module.ts详解、以及Angular中创建组件、组件详解、 绑定数据
目录结构分析
文件 说明
|--E2e 应用的端对端(e2e)测试,用 Jasmine 写成并用 protractor 端对端测试运行器测试。
|--Node_modules 依赖包
|--Src
|--App Angular应用文件
|--App.module.ts
|---App.component.ts
|--assets 资源文件
|--environments 环境配置:开发、部署
|--index.html 应用的宿主页面。 它以特定的顺序加载一些基本脚本。 然后它启动应用,将根AppComponent放置到自定义<my-app>标签里。
|--main.ts 项目的入口文件
|--polyfills.ts 处理浏览器兼容问题
|--angular.json Cli配置文件
|--.editorconfig 统一代码风格工具配置,不支持的需要安装插件
|--.gitignore Git配置文件
|--karma.conf.js 在测试指南中提到的 karma 测试运行器的配置。
|--package.json 项目指定npm依赖包
|--tsconfig.app.json Typescript编译配置
|--tsconfig.spec.json Typescript测试编译配置
|--tsconfig.json Typescript编译配置
|--tslint.json Typescript语法检查器详情参考:https://www.angular.cn/guide/file-structure
app.module.ts、组件分析
app.module.ts
定义 AppModule,这个根模块会告诉 Angular 如何组装该应用。 目前,它只声明了 AppComponent。 稍后它还会声明更多组件。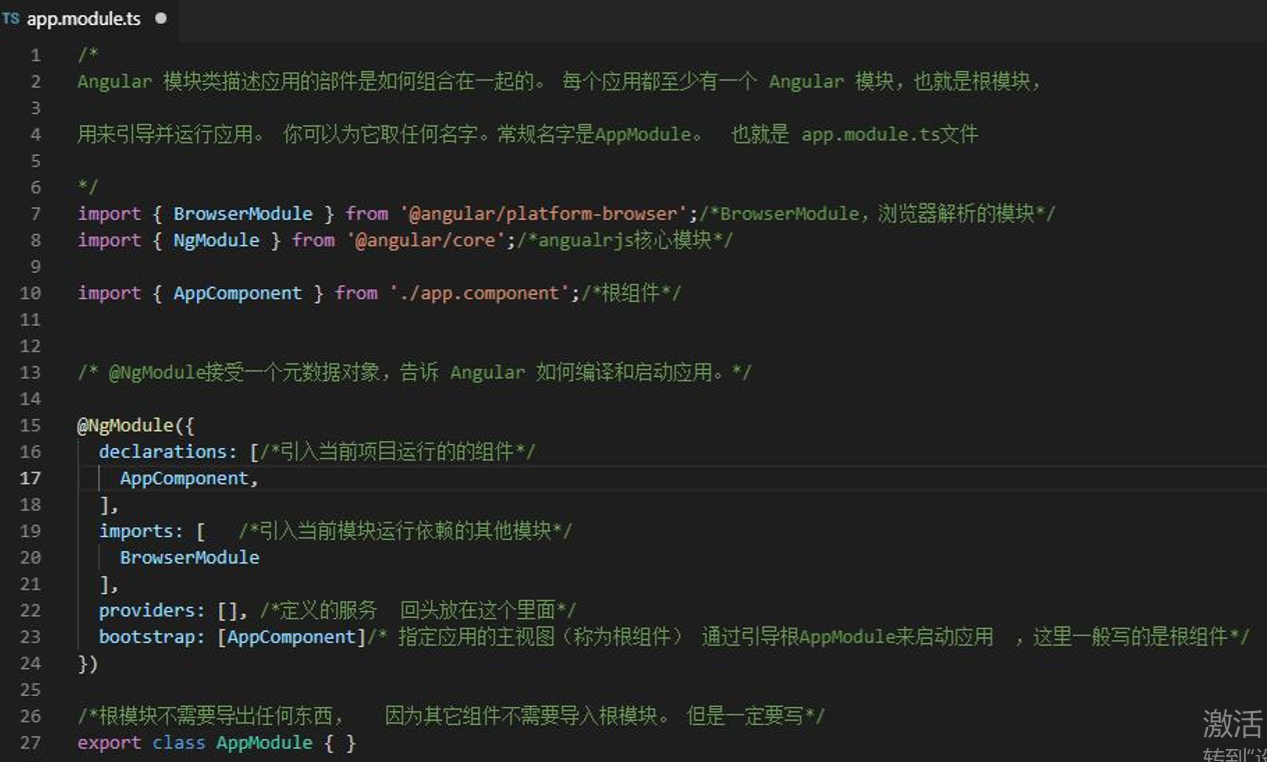
自定义组件
https://cli.angular.io/
创建组件:
ng g component components/header 组件内容详解:
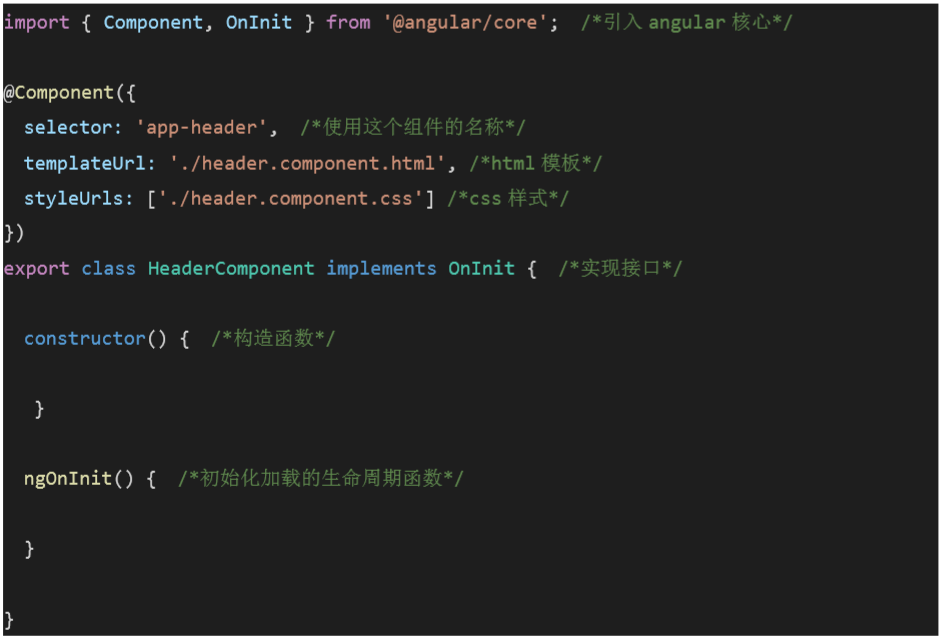
app.component.ts组件分析
Angular应用中,模板指的的是@Component装饰器的template或templateUrl指向的HTML页面 例如:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
interface Course {
id:number,
description:string
}
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
// templateUrl: './app.component.html',
template:`
<div class="course">
<span class="description">{{courseObj.description}}</span>
</div>
`,
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent{
title = 'ng-module-routes';
id:number = 1;
description:string = 'sss';
public courseObj: Course = {
id: 1,
description: "Angular For Beginners"
};
}很明显Angular不是简单地用一个字符串来处理模板。 那么这是如何工作的?
Angular不会生成HTML字符串,它直接生成DOM数据结构
实际上,Angular把组件类中的数据模型应用于一个函数(DOM component renderer)。 该函数的输出是对应于此HTML模板的DOM数据结构。
一旦数据状态发生改变,Angular数据检测器检测到,将重新调用 该DOM component renderer。
mvvm
Mvvm定义MVVM是Model-View-ViewModel的简写。即模型-视图-视图模型。
【模型】指的是后端传递的数据。
【视图】指的是所看到的页面。
【视图模型】mvvm模式的核心,它是连接view和model的桥梁。
它有两个方向:
一是将【模型】转化成【视图】,即将后端传递的数据转化成所看到的页面。实现的方式是:数据绑定。
二是将【视图】转化成【模型】,即将所看到的页面转化成后端的数据。
实现的方式是:DOM 事件监听。这两个方向都实现的,我们称之为数据的双向绑定。
总结
在MVVM的框架下视图和模型是不能直接通信的。它们通过ViewModel来通信,ViewModel通常要实现一个observer观察者,当数据发生变化,ViewModel能够监听到数据的这种变化,然后通知到对应的视图做自动更新,而当用户操作视图,ViewModel也能监听到视图的变化,然后通知数据做改动,这实际上就实现了数据的双向绑定。
并且MVVM中的View 和 ViewModel可以互相通信。MVVM流程图如下: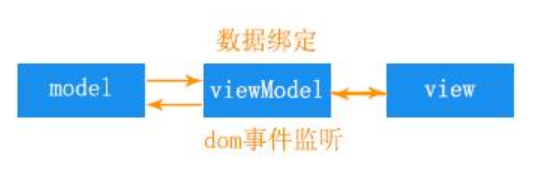
angular 组件 以及组件里面的模板
Angular 绑定数据
数据文本绑定
Angular 中使用{{}}绑定业务逻辑里面定义的数据
{{}}
<div class="title"> {{title}}</div>
{{userinfo.username}} {{message}} {{student}}angualr模板里面绑定属性
<div [title]="student">
张三
</div>angualr模板里面绑定Html
<span [innerHTML]='content' class="red"></span>angualr模板里面允许做简单的运算
1+2={{1+2}}数据循环 *ngFor
*ngFor 普通循环
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let item of list">{{item}}</li>
</ul>循环的时候设置 key
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let item of list;let key=index;">
{{key}}---{{item.title}}
</li>
</ul>条件判断语句 *ngIf
<div *ngIf="flag">
<img src="assets/images/02.png" />
</div>
<div *ngIf="!flag">
<img src="assets/images/01.png" />
</div>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let item of list;let key=index;">
<span *ngIf="key==1" class="red">{{key}}---{{item.title}}</span>
<span *ngIf="key!=1">{{key}}---{{item.title}}</span>
</li>
</ul>条件判断语句 *ngSwitch
<span [ngSwitch]="orderStatus">
<p *ngSwitchCase="1">
表示已经支付
</p>
<p *ngSwitchCase="2">
支付并且确认订单
</p>
<p *ngSwitchCase="3">
表示已经发货
</p>
<p *ngSwitchCase="4">
表示已经收货
</p>
<p *ngSwitchDefault>
无效订单
</p>
</span>属性[ngClass]
<div class="red">
ngClass演示 (尽量不要用dom来改变class)
</div>
<div [ngClass]="{'blue':true,'red':false}">
ngClass演示
</div>
<div [ngClass]="{'orange':flag,'red':!flag}">
ngClass演示
</div>
<strong>循环数组,让数组的第一个元素的样式为red ,第二个为orange,第三个为blue</strong>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let item of list;let key=index;" [ngClass]="{'red':key0,'orange':key1,'blue':key==2}">
{{key}}---{{item.title}}
</li>
</ul>属性[ngStyle]
<p style="color:red">我是一个p标签</p>
<p [ngStyle]="{'color':'blue'}">我是一个p标签</p>
<p [ngStyle]="{'color': attr}">我是一个p标签 </p>管道
类似于vue2的filtter
{{today | date:'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm ss'}}执行事件(click)
home.component.html
<strong>{{title}}</strong>
<button (click)="run()">执行事件</button>
<button (click)="setData()">执行方法改变属性里面的数据</button>
<button (click)="runEvent($event)">执行方法获取事件对象</button>home.component.ts
run(){
console.log('这是一个自定义方法')
console.log(this.title);
}
setData(){
this.title='我是一个改变后的title';
}
// $event
runEvent(event){
//ionic必须这样写
let dom:any=event.target;
dom.style.color="red";
}表单事件 事件对象
home.component.ts
keyDown
<input type="text" (keydown)="keyDown($event)" />
<br>
keyUp:
<input type="text" (keyup)="keyUp($event)" />home.component.ts
keyDown(e){
if(e.keyCode==13){
console.log('按了一下回车')
}else{
//e.target 获取dom对象
console.log(e.target.value);
}
}
keyUp(e){
if(e.keyCode==13){
console.log(e.target.value);
console.log('按了一下回车');
}
}双向数据绑定--MVVM 只是针对表单
<input [(ngModel)]="inputValue">在app.module.ts导入FormsModule
并在imports导入
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
....
imports: [ /*配置当前模块运行依赖的其他模块*/
FormsModule
],使用:
<input type="text" [(ngModel)]='keywords' />
{{keywords}}
<button (click)="changeKeywords()">改变keywords的值</button>Angular的标签
ng-container
ng-content
ng-template
ng-container
TIP:
它等用于vue中的<template></template>,react中的<></>, ng-container是一种特殊的元素,可以保存结构指令(比如 ng-if),而无需向DOM添加新元素。
简而言之:ng-container标签,不会在dom中产生标签
<ng容器>允许我们在没有任何额外元素的情况下使用结构指令,确保唯一应用的DOM更改是由指令本身决定的。这不仅提高了性能(甚至稍微提高了一点),因为浏览器最终呈现的元素更少,而且在拥有更干净的DOM和样式方面也是一项宝贵的资产。例如,它可以使我们能够使用结构指令,而不破坏依赖于精确DOM结构的样式(例如,我们在使用flex容器、边距、子组合选择器等时获得的样式)。
ng-content
插槽,插入的内容,插入到指定的位置。
<ng-content>元素指定在组件模板中投影内容的位置。
在一个子组件里,定义具名插槽:
<div>
<div>111</div>
<ng-content select="[ ]"></ng-content>
<div>333</div>
</div>在父组件里,引入该组件
app-child使用插槽,可以这么写
<app-child>
<div importSlot>
222
</div>
</app-child>最终页面呈现的就是:111 222 333
ng-template
使用<ng template>,您可以定义仅当您直接或间接明确指示Angular渲染时才由Angular渲染的模板内容,从而可以完全控制内容的显示方式和时间。请注意,如果您在<ng模板>中包装内容,而不指示Angular渲染它,则此类内容不会出现在页面上。例如,请参见下面的HTML代码,当处理它时,Angular不会在短语“Hip!Hip!Hooray!”中呈现中间的“Hip”,因为周围的<ng template>。
Angular 配置文件常见配置注解
angular.json, 这个文件是整个项目的概要,包含了 不同的环境,测试、代理、第三方资源 和 众多内置工具。
angular.json
{
"$schema": "./node_modules/@angular/cli/lib/config/schema.json", //angular-cli.json规则文件
"version": 1, // 指明了Angular 工作空间 概要的版本。
"newProjectRoot": "projects",//定义了由CLI创建的新的内部应用和库放置的位置。默认值为`projects`
"projects": { //包含了工作空间中所有项目的配置信息。
"angularTest": { //项目配置详情(项目名称)
"root": "", //指定了项目文件的根文件夹,可能为空,但是它指定了一个特定的文件夹。
"sourceRoot": "src",//指定了项目源文件位置
"projectType": "application",//表明了 项目的状态 是 `appliaction`还是`library`。
"prefix": "app",//当CLI创建 `component`或者`directive`时,使用该属性来区别他们。组件selector默认前缀
"schematics": {},
"architect": {//自定义自动化命令
"build": { //build模块配置
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:browser",//build执行的自动化程序
"options": {
"outputPath": "dist/angularTest",//编译后的输出目录,默认为dist
"index": "src/index.html", //指定首页文件,默认值为"index.html"
"main": "src/main.ts", //指定应用的入门文件
"polyfills": "src/polyfills.ts",// 指定polyfill文件
"tsConfig": "src/tsconfig.app.json",//指定tsconfig文件
"assets": [ //记录资源文件夹,构建时复制到`outDir`指定的目录
"src/favicon.ico",//网站ico图标
"src/assets"
],
"styles": [//引入全局样式,构建时会打包进来,常用于第三方库引用样式
"src/styles.css"
],
"scripts": [ ]// 引入全局脚本,构建时会打包进来,常用语第三方库引入的脚本
},
"configurations": {//代表这个命令的多种调用模式
"production": {//打包命令-–prod()的配置
"fileReplacements": [
{
"replace": "src/environments/environment.ts",
"with": "src/environments/environment.prod.ts"
}
],
"optimization": true,
"outputHashing": "all",
"sourceMap": false,
"extractCss": true,
"namedChunks": false,
"aot": true,
"extractLicenses": true,
"vendorChunk": false,
"buildOptimizer": true
}
}
},
"serve": {//serve模块配置
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:dev-server",//serve执行的自动化程序
"options": {
"browserTarget": "angularTest:build"
},
"configurations": {
"production": {
"browserTarget": "angularTest:build:production"
}
}
},
"extract-i18n": {
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:extract-i18n",
"options": {
"browserTarget": "angularTest:build"
}
},
"test": {
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:karma",
"options": {
"main": "src/test.ts",
"polyfills": "src/polyfills.ts",
"tsConfig": "src/tsconfig.spec.json",
"karmaConfig": "src/karma.conf.js",
"styles": [
"src/styles.css"
],
"scripts": [],
"assets": [
"src/favicon.ico",
"src/assets"
]
}
},
"lint": {
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:tslint",
"options": {
"tsConfig": [
"src/tsconfig.app.json",
"src/tsconfig.spec.json"
],
"exclude": [
"**/node_modules/**"
]
}
}
}
},
"angularTest-e2e": { //项目测试详细配置
"root": "e2e/",
"projectType": "application",
"architect": {
"e2e": {
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:protractor",
"options": {
"protractorConfig": "e2e/protractor.conf.js",
"devServerTarget": "angularTest:serve"
},
"configurations": {
"production": {
"devServerTarget": "angularTest:serve:production"
}
}
},
"lint": {
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:tslint",
"options": {
"tsConfig": "e2e/tsconfig.e2e.json",
"exclude": [
"**/node_modules/**"
]
}
}
}
}
},
"defaultProject": "angularTest"//当使用CLI命令时,`defaultProject`代表显示的名字。
}组件通信
@input-父传子
父组件html中:
<Cscore-set #Cscore (init3)="init3($event)" [(leftTreeList3)]="leftTreeList3"></Cscore-set>#Cscore 获取当前组件实例,类似于vue的ref
init3 传的事件
leftTreeList3 传的参数
父组件js中:
leftTreeList3 = [] //在constructor上面定义变量,改变量传给子组件,也可以自己使用
@ViewChild('Cscore', { static: false }) Cscore; //子组件实例
/**
* 左侧列表
* options为配置项
* @param options -focusedRowIndex :this.treeInstance.focusedRowIndex = -1;
* @param options -saveCreate 保存时是否为新增 :true||false
*/
async init3(options: any = {}) {
//函数里怎么写却决于你的业务,这里删掉了一些业务代码,下面代码业务上不成立,仅用来展示怎么使用
//对数组中对象去重
var obj = {};
res = res.reduce(function (item, next) {
obj[next.BreedingID] ? '' : obj[next.BreedingID] = true && item.push(next);
return item;
}, []);
this.leftTreeList3 = res
//调用子组件的方法
this.Cscore.setDeficiencyID(this.leftTreeList3)
//更改子组件的变量赋值
this.Cscore.allowDelete = true
}子组件js中:
在接受leftTreeList3的值的时候,使用了@Input() set 跟函数是因为可以检测到这个变量的变化,然后赋值,函数内也可以做一些自己的业务,类似于vue的watch监听。
@Output 用于接父组件的方法,@Output 的本质是事件机制,我们可以利用它来监听子组件上派发的事件,子组件上这样写。
EventEmitter:在angular中组件通过定义EventEmitter 事件弹射器的方式由子组件向父组件发送数据。
代码:
import { Component, OnInit, ViewChild, Input, OnChanges, SimpleChanges, Output, EventEmitter } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'Cscore-set',
templateUrl: './Cscore.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./Cscore.component.scss'],
})
export class Cscore implements OnInit {
allowDelete: boolean;
leftTreeList: any = [] //左侧传的列表
//子接父传值,接受传值类似于watch监听,
@Input() set leftTreeList3(val) {
this.leftTreeList = val
};
@Output() init3 = new EventEmitter();
//在class里面接收,下面变量不成立,仅作模拟
@Input('model') model;
constructor(
private service: BreedingSetService,
private tokenService: TokenAuthService,
){
}
delete() {
//触发父组件的函数,.emit为固定的写法,括号里面为我们业务上的传值
this.init3.emit({ focusedRowIndex: true })
}
}@ViewChild-直接调用
通过 @ViewChild父组件直接调用子组件方法或修改变量 然后就可以通过this.compDemo获取这个子组件了,
注意
需要注意的是,如果使用了*ngIf去控制该组件渲染时,this.Cscore未加载的时候调用相应的方法会报错, 这里可以开启宏任务后再去做相应业务,比如在setTimeout回调里写。
父组件 引入
import { ViewChild } from '@angular/core';在子组件上
<compDemo #compDemo> </compDemo>加一个#号;通过#在父组件class内部,利用属性装饰器ViewChild,和刚才的子组件关联起来
@ViewChild('compDemo', { static: false }) compDemo: any;@Output 子调父
子组件通过-@Output触发父组件的方法
演示例子: 父组件:news 子组件:footer
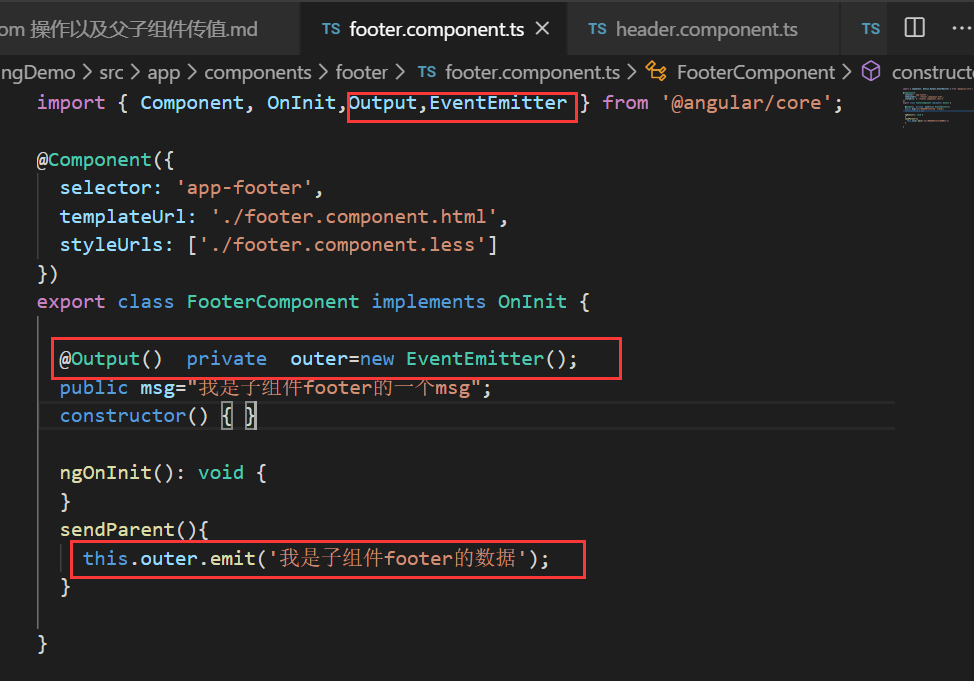
子组件引入 Output 和 EventEmitter
import { Component, OnInit ,Input,Output,EventEmitter} from '@angular/core';子组件中实例化 EventEmitter
@Output()
private outer=new EventEmitter<string>();
/*用 EventEmitter 和 output 装饰器配合使用 <string>指定类型变量*/子组件通过 EventEmitter 对象 outer 实例广播数据
sendParent(){
this.outer.emit('msg from child')
}
父组件调用子组件的时候,定义接收事件,outer 就是子组件的 EventEmitter 对象 outer
<!-- data就是 子组件给父组件的数据 outer是定义的事件名称-->
<app-footer (outer)="getFooterRun(data)"></app-footer>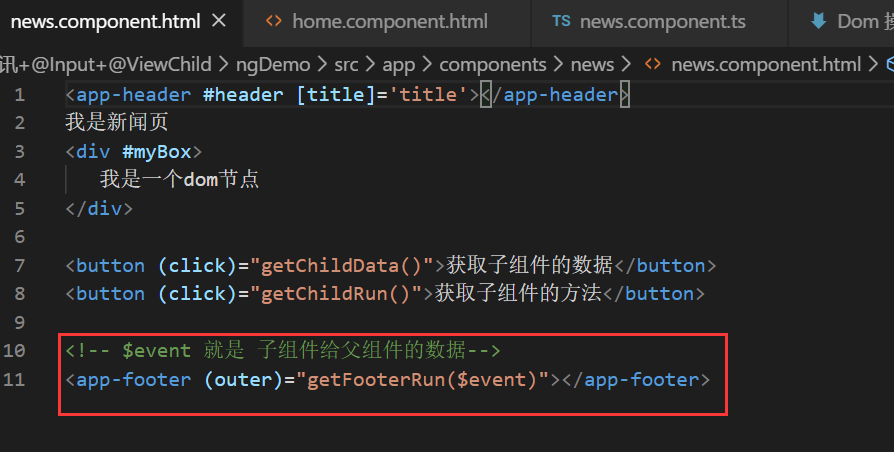
父组件接收到数据会调用自己的 getFooterRun 方法,这个时候就能拿到子组件的数
//接收子组件传递过来的数据
getFooterRun(data){
console.log(data);
}非父子组件通讯
公共的服务
Localstorage(推荐)
Cookie
总结
vue中 关于$emit的用法
父组件可以使用属性把数据传给子组件,子组件通过props接受。
子组件可以使用 $emit 触发父组件的自定义事件。
vm.$emit( event, arg ) //触发当前实例上的事件
vm.$on( event, fn );//监听event事件后运行 fn;
angular中 关于emit的用法
父组件可以使用属性把数据传给子组件,子组件通过@input接受。
子组件可以使用 Output 和 EventEmitter 触发父组件的自定义事件。
父组件
<app-footer (event)="getFooterRun(data)"></app-footer>子组件
@Output()
private event=new EventEmitter<string>();
/*用 EventEmitter 和 output 装饰器配合使用 <string>指定类型变量*/
sendParent(){
// outer 相当于是事件名称
this.event.emit(data)
}
<button (event)="sendParent()">通过@Output给父组件广播数据</button>生命周期函数
官方文档:https://www.angular.cn/guide/lifecycle-hooks
生命周期函数通俗的讲就是组件创建、组件更新、组件销毁的时候会触发的一系列的方法。 当 Angular 使用构造函数新建一个组件或指令后,就会按下面的顺序在特定时刻调用这些 生命周期钩子方法
TIP
一、constructor (非生命周期函数)
二、ngOnChanges()
三、ngOnInit()
四、ngDoCheck()
五、ngAfterContentInit()
六、ngAfterContentChecked()
七、ngAfterViewInit()
八、ngAfterViewChecked()
九、ngOnDestroy()
constructor
构造函数中除了使用简单的值对局部变量进行初始化 之外,什么都不应该做。 (非生命周期函数) constructor适用场景 constructor中应该只进行依赖注入而不是进行真正的业务操作
import { RequestService } from '../../services/request.service';
.......
//使用构造注入方式,注入服务
constructor(public request:RequestService) { }ngOnChanges()
当 Angular(重新)设置数据绑定输入属性时响应。 该 方法接受当前和上一属性值的 SimpleChanges 对象 当被绑定的输入属性的值发生变化时调用,首次调用一 定会发生在 ngOnInit() 之前。
当被绑定的输入属性的值发生变化时调用(父子组件传值的时候会触发)
ngOnInit()
在 Angular 第一次显示数据绑定和设置指令/组件的输入属性之后,初始化指令/组件。 在第一轮 ngOnChanges() 完成之后调用,只调用一次。 使用 ngOnInit() 有两个原因:
在构造函数之后马上执行复杂的初始化逻辑
在 Angular 设置完输入属性之后,对该组件进行准备。 有经验的开发者会认同组件的构建应该很便宜和安全。
请求数据一般放在这个里面
ngDoCheck()
检测,并在发生 Angular 无法或不愿意自己检测的变化时作出反应。在每个 Angular 变更检测周期中调用, ngOnChanges() 和 ngOnInit()之后。
检测,并在发生 Angular 无法或不愿意自己检测的变化时作出反应
ngAfterContentInit()
当把内容投影进组件之后调用。第一次 ngDoCheck() 之 后调用,只调用一次。 当把内容投影进组件之后调用
ngAfterContentChecked()
每次完成被投影组件内容的变更检测之后调用。 ngAfterContentInit() 和每次 ngDoCheck() 之后调用。
ngAfterViewInit()
视图加载完成以后触发的方法,初始化完组件视图及其子视图之后调用。第一次 ngAfterContentChecked()之后调用,只调用一次。 初始化完组件视图及其子视图之后调用(dom操作放在这个里面)
ngAfterViewChecked()
每次做完组件视图和子视图的变更检测之后调用。 ngAfterViewInit()和每次 ngAfterContentChecked() 之后 调用
ngOnDestroy()
当 Angular 每次销毁指令/组件之前调用并清扫。在这 儿反订阅可观察对象和分离事件处理器,以防内存泄 漏。 在 Angular 销毁指令/组件之前调用。
父传子的而一种方式
父
<app-refs [block]="aaa" views="aaa"></app-refs>
ts
public aaa=1;
子组件
@Component({
selector: 'app-refs',
templateUrl: './refs.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./refs.component.less'],
inputs: ['block','v:views'],
})
public block;
public v;
ngOnInit(): void {
console.log(this.block);
console.log(this.v);
}子传父的另一种方式
父
<app-refs (a)="onEvery($event)" (b)="onFive($event)"></app-refs>
onEvery(e){
console.log(e);
}
onFive(e){
console.log(e);
}
子
@Component({
outputs: ['a', 'c:b']
})
public a = new EventEmitter();
public c = new EventEmitter();
ngOnInit(): void {
this.a.emit('333');
this.c.emit('444');
}Angular 中的数据交互(get,post)
HttpClientModule
axios
Angular get 请求数据
Angular5.x 以后 get、post 和和服务器交互使用的是 HttpClientModule 模块
在 app.module.ts 中引入 HttpClientModule 并注入
import {HttpClientModule} from '@angular/common/http'
imports: [ BrowserModule, HttpClientModule ]在用到的地方引入 HttpClient 并在构造函数声明
import {HttpClient} from "@angular/common/http";
constructor(public http:HttpClient) { }get 请求数据
var api = "http://localhost:3000/info";
this.http.get(api).subscribe(response => {
console.log(response);
});Angular post 提交数据
Angular5.x 以后 get、post 和和服务器交互使用的是 HttpClientModule 模块。
在 app.module.ts 中引入 HttpClientModule 并注入
import {HttpClientModule} from '@angular/common/http';
imports: [ BrowserModule, HttpClientModule ]在用到的地方引入 HttpClient、HttpHeaders 并在构造函数声明 HttpClient
import {HttpClient,HttpHeaders} from "@angular/common/http";
constructor(public http:HttpClient) { }post 提交数据
const httpOptions={
headers:newHttpHeaders({'Content-Type':'application/json'})
};
var api="http://127.0.0.1:3000/doLogin";
this.http.post(api,{username:'张三',age:'20'},httpOptions).subscribe(response=>{
console.log(response);
});axios 请求数据
安装 axios yarn add axios -D
用到的地方引入 axios import axios from 'axios';
看文档使用
axios.get('/user?ID=12345')
.then(function(response){
//handle success
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error){
//handle error
console.log(error);
})
.then(function(){
//always executed
});Angular 中的路由
命令创建项目
ng new ng-demo --skip-install
创建需要的组件
ng g component components/home
ng g component components/news
ng g component components/newscontent找到 app-routing.module.ts 配置路由
引入组件
import { HomeComponent } from './components/home/home.component';
import { NewsComponent } from './components/news/news.component';
import { ProductComponent } from './components/product/product.component';配置路由
const routes: Routes = [
{path: 'home', component: HomeComponent},
{path: 'news', component: NewsComponent},
{path:'product', component:ProductComponent },
{path: '*', redirectTo: '/home', pathMatch: 'full' }
];找到 app.component.html 根组件模板,配置 router-outlet 显示动态加载的路由
<h1>
<a routerLink="/home">首页</a>
<a routerLink="/news">新闻</a>
</h1>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>routerLink 跳转页面默认路由
<a routerLink="/home">首页</a>
<a routerLink="/news">新闻</a>
//匹配不到路由的时候加载的组件 或者跳转的路由
{
path: '**', /*任意的路由*/
// component:HomeComponent
redirectTo:'home'
}routerLinkActive
设置 routerLink 默认选中路由
<h1>
<a routerLink="/home" routerLinkActive="active">
首页
</a>
<a routerLink="/news" routerLinkActive="active">
新闻
</a>
</h1>
<h1>
<a [routerLink]="[ '/home' ]" routerLinkActive="active">首页</a>
<a [routerLink]="[ '/news' ]" routerLinkActive="active">新闻</a>
</h1>动态路由
问号传参
跳转方式,页面跳转或js跳转 问号传参的url地址显示为 …/list-item?id=1
页面跳转 queryParams属性是固定的
<a [routerLink]="['/list-item']" [queryParams]="{id:item.id}">
<span>{{ item.name }}</span>
</a>//js跳转-router为ActivatedRoute的实例
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
constructor(private router: Router) {}
this.router.navigate(['/newscontent'],{
queryParams:{
name:'laney',
id:id
},
skipLocationChange: true
//可以不写,默认为false,设为true时路由跳转浏览器中的url会保持不变,传入的参数依然有效
});获取参数方式
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
constructor(public route:ActivatedRoute) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.route.queryParams.subscribe((data)=>{
console.log(data);
})
}路径传参
路径传参的url地址显示为 …/list-item/1
<!-- 页面跳转 -->
<a [routerLink]="['/list-item', item.id]">
<span>{{ item.name }}</span>
</a>js跳转-router为ActivatedRoute的实例
this.router.navigate(['/list-item', item.id]);路径配置: {path: 'list-item/:id', component: ListItemComponent}
获取参数方式
this.route.params.subscribe(
param => {
this.id= param['id'];
}
)父子路由
创建组件引入组件
import { WelcomeComponent } from './components/home/welcome/welcome.component';
import { SettingComponent } from './components/home/setting/setting.component';配置路由
{
path:'home',
component:HomeComponent,
children:[{
path:'welcome',
component:WelcomeComponent
},{
path:'setting',
component:SettingComponent
},
{path: '**', redirectTo: 'welcome'}
]
},父组件中定义router-outlet
<router-outlet></router-outlet>Angular 内置模块
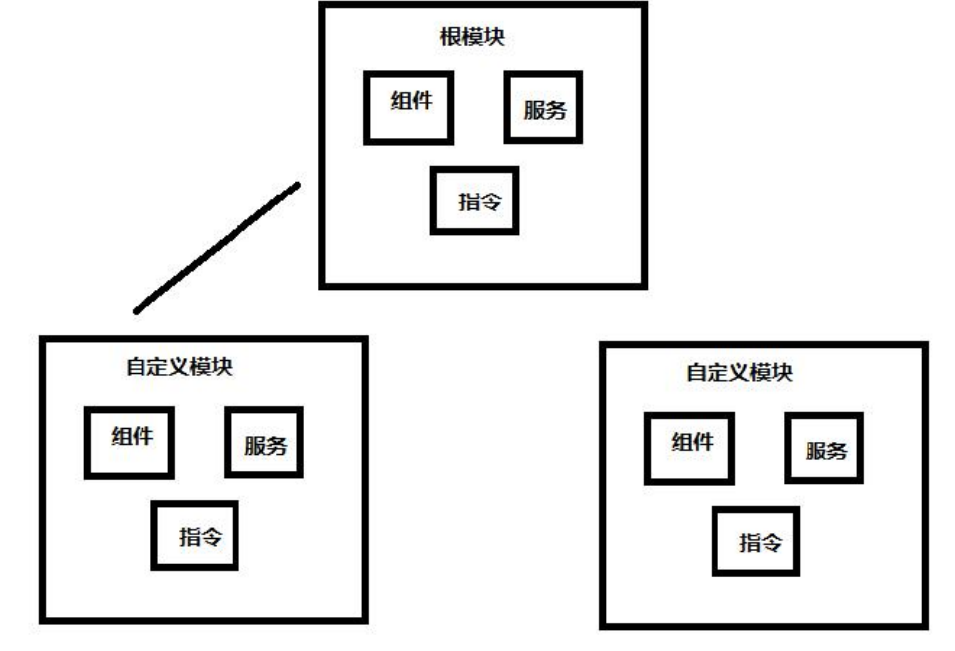
Angular 自定义模块
当我们项目比较小的时候可以不用自定义模块。但是当我们项目非常庞大的时候把所有的组件都挂载到根模块里面不是特别合适。所以这个时候我们就可以自定义模块来组织我们的项目。并且通过 Angular自定义模块可以实现路由的懒加载。
ng g module mymodule
新建一个 user 模块
ng g module module/user
新建一个 user 模块下的根组件
ng g component module/user
新建一个 user 模块下的 address,order,profile 组件
ng g component module/user/components/address
ng g component module/user/components/order
ng g component module/user/components/profile@NgModule的理解
举例说明,如果一个angular应用是一个公司,那么AppModule就是这个公司。AppComponent就是这个公司的一个工厂,公司可以有很多个工厂。declearation数组里面的元素就是组成工厂的一部分,比如生产车间、人员管理系统等。imports数组就像是工厂请来的外援,专业性比较强。providers数组就像是后勤部门,提供各种服务。
Angular的基本构造块就是NgModule,它会把一部分的代码整合在一起,可以看做一个一个的单元块,在使用脚手架搭建Angular项目时,会自动的生成一个根目录模块AppModule,根模块有一个根组件AppComponent,引导这个根模块就可以启动应用了,Angular应用是模块化的,每一个模块都可以根据需求去包含任意的组件。
providers:将本模块所有在组件中注入的服务(接口),在这里提前定义好,否则在此模块中使用这个服务会有错误提示。
declaration:声明一些模块中要使用到的一些组件,指令,管道等。
imports:导入一些模块,比如说我把所有的指令构成一个模块 我使用其中某些指令的时候,我可以选择导入整个指令模块。也可以导入一些通过npm install 安装的一些模块导入其中,才可以使用。
exports:导出组件or指令管道等,以供引用此模块的模块可以使用此模块的组件or 指令管道等。
exporyComponents:entry component 表示 angular 的入口组件,可以引导组件是一个入口组件,Angular 会在引导过程中把它加载到 DOM 中。 其它入口组件是在其它时机动态加载的。字面上的意义,但是啥时候用呢,比如,我要弹出一个组件,那么这个组件是要动态加载到DOM中了吧,这个时候就需要将这个组件xxxComponent写上了。
bootstrap:这个模块启动的时候应该启动的组件,上面代码可以看到AppModule是作为根模块的启动组件。
schemas:不属于Angular的组件或者指令的元素或者属性都需要在这里进行声明。
以下为我平时开发时写的代码举例 breeding-set.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { BreedingSettingComponent } from './breeding-set.component';
import { inheritance } from './Ainheritance/inheritance.component';
import { Cscore } from './Cscore/Cscore.component';
import { Bchoice } from './Bchoice/Bchoice.component';
import { TypeSettingRoutingModule } from './breeding-set.routing';
import {
DxTreeViewModule,
DxFormModule,
DxToolbarModule,
DxButtonModule,
DxTreeListModule,
DxTextAreaModule,
DxRadioGroupModule,
DxSelectBoxModule,
DxValidationGroupModule,
DxDateBoxModule,
DxPopupModule,
DxDataGridModule,
DxValidatorModule,
DxDropDownBoxModule,
DxTagBoxModule,
} from 'devextreme-angular';
import { BreedingSetService } from './breeding-set.service';
import { TranslateModule } from 'src/app/providers/i18n-translate';
@NgModule({
imports: [// 用来导入外部模块
CommonModule,
TypeSettingRoutingModule,
DxTreeViewModule,
DxFormModule,
DxToolbarModule,
DxButtonModule,
DxTreeListModule,
DxTextAreaModule,
DxRadioGroupModule,
TranslateModule,
DxSelectBoxModule,
DxValidationGroupModule,
DxDateBoxModule,
DxPopupModule,
DxDataGridModule,
DxValidatorModule,
DxTagBoxModule,
DxDropDownBoxModule,
],
declarations: [BreedingSettingComponent, inheritance, Cscore, Bchoice],// 用来放组件、指令、管道的声明
providers: [BreedingSetService],// 需要使用的 Service(接口)
})
export class BreedingSetModule { }举例:挂载模块与创建服务
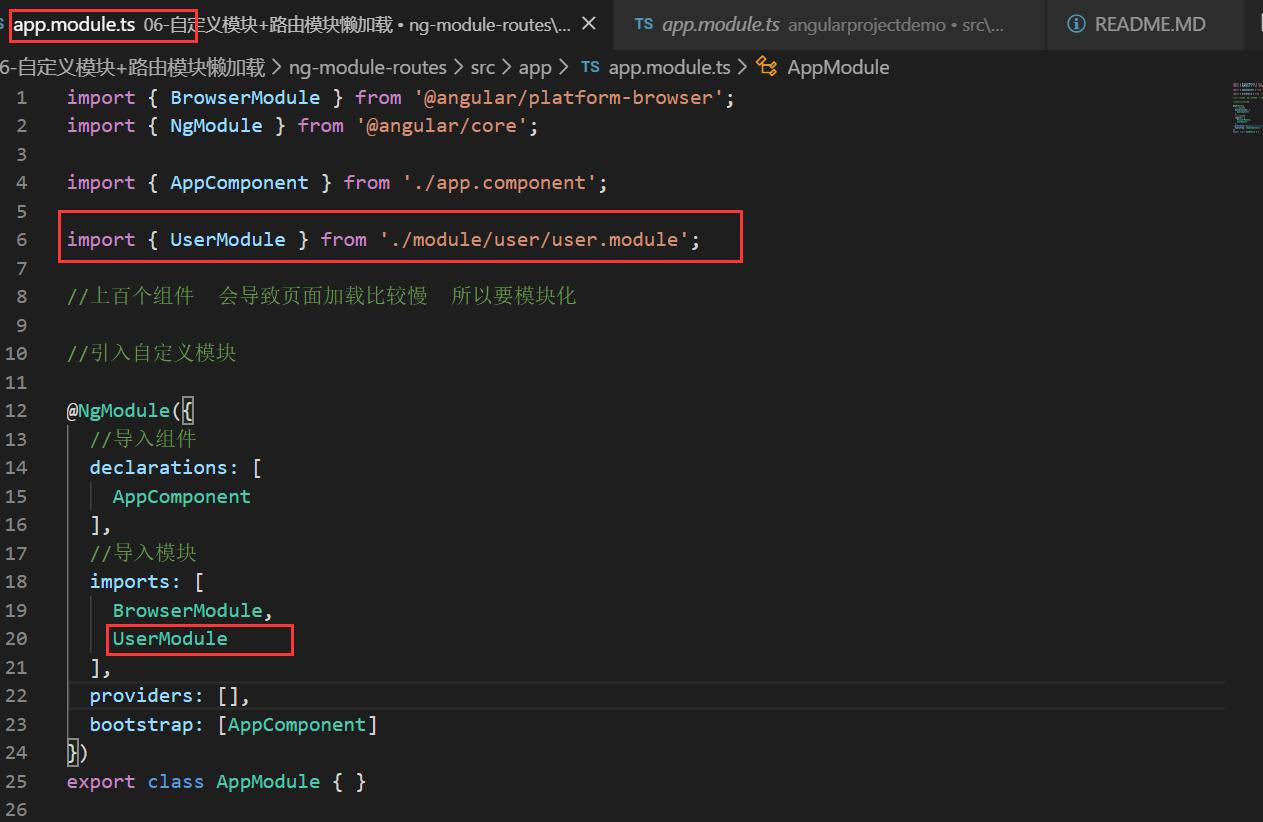
如何在根模块挂载 user 模块呢?
在 app 根组件的模板文件 app.component.html 里引用 user 组件会报错 需要如下处理才可以被访问
在 app.module.ts 引入模块
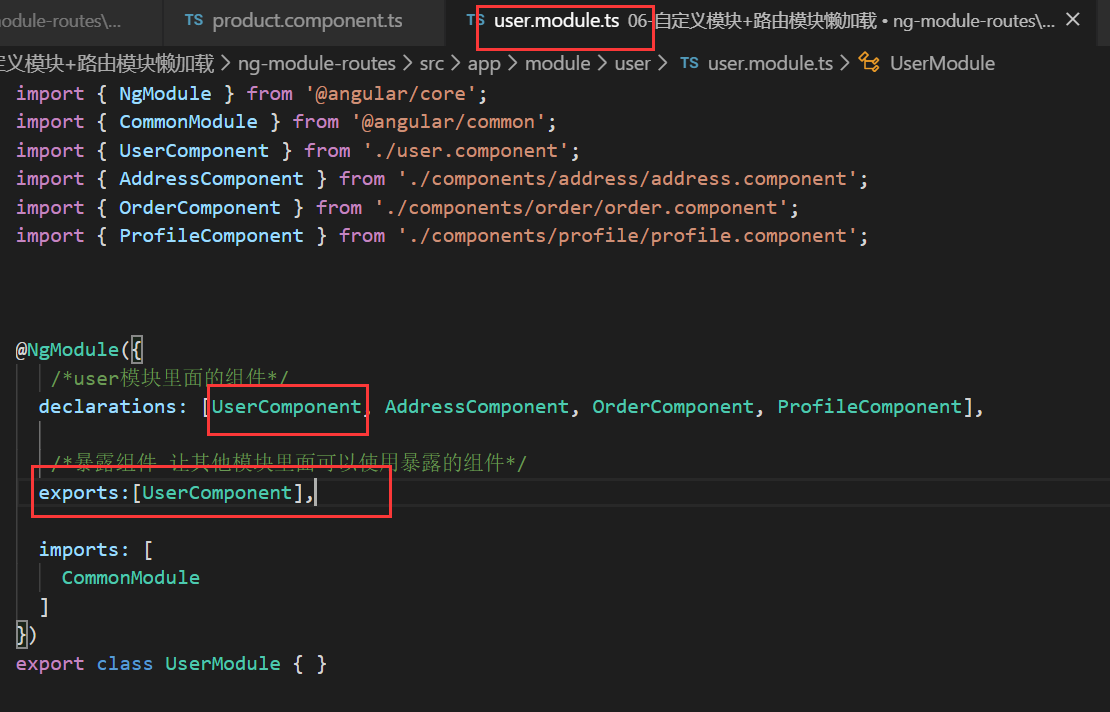
user 模块暴露出 要被外界访问到的组件
在根模板 app.component.html 里引入
<app-user></app-user>如果需要在根组件里直接 使用 app-address 组件,也是需要先在 user 模块 user.module.ts 暴露
/暴露组件 让其他模块里面可以使用暴露的组件/
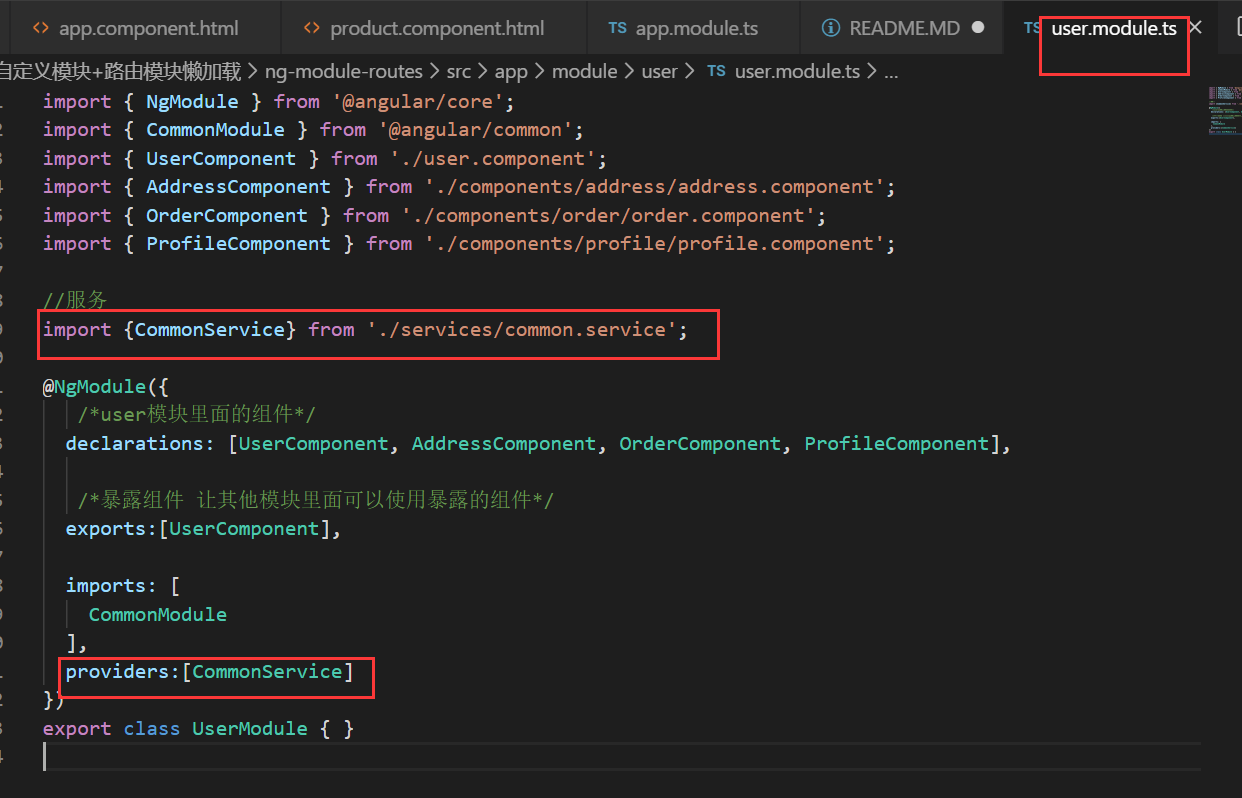
exports:[UserComponent,AddressComponent]创建 user 模块下的服务
创建 ng g service module/user/services/common
在 user 模块引入服务
配置路由实现模块懒加载
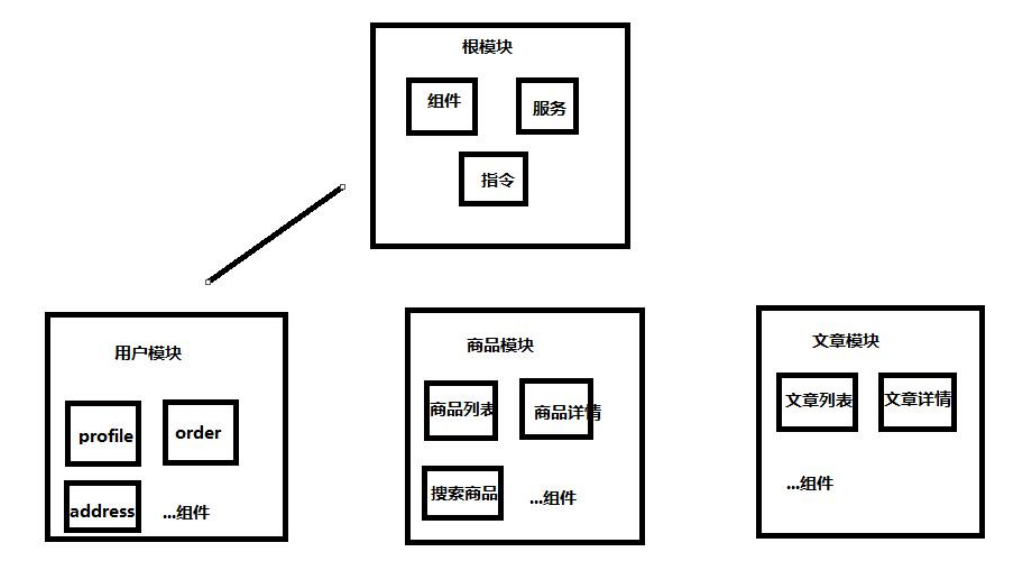
创建模块:
ng g module module/user --routing
ng g module module/article --routing
ng g module module/product --routing
创建组件:
ng g component module/user
ng g component module/user/components/profile
ng g component module/user/components/order
ng g component module/article
ng g component module/article/components/articlelist ng g component module/article/components/info
ng g component module/product
ng g component module/product/components/plist
ng g component module/product/components/pinfoangular配置懒加载
在angular中路由即能加载组件又能加载模块,而我们说的懒加载实际上就是加载模块,目前还没有看到懒加载组件的例子。 加载组件使用的是component关键字 加载模块则是使用loadChildren关键字

1. 在app文件夹下 新建 app-routing.module.ts
内容如下:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }forRoot是用在根模块加载路由配置, 而forChild是用在子模块加载路由配置。
注意:需要在根模板 app.module.ts里导入AppRoutingModule模块
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
...
imports: [
AppRoutingModule,
]在子模块里配置路由
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
// import {ArticleComponent} from './article.component';
const routes: Routes = [
// {
// path:'',
// component:ArticleComponent
// }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forChild(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class ArticleRoutingModule { }也可以在新建项目的时候 就把路由的模块加上,可以省去上面的配置
在 article模块的 article-routing.module.ts配置路由
import {ArticleComponent} from './article.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path:'',
component:ArticleComponent
}
];在app的路由模块进行配置路由
const routes: Routes = [
{
path:'article',
//写法一:
loadChildren:'./module/article/article.module#ArticleModule'
//写法二
// loadChildren: () => import('./module/user/user.module').then( m => m.UserModule)
},
// {
// path:'user',loadChildren:'./module/user/user.module#UserModule'
// },
// {
// path:'product',loadChildren:'./module/product/product.module#ProductModule'
// },
{
path:'**',redirectTo:'article'
}
];如果在之前新建模块的时候没有加上--routing,,需要配置模块的路由
product模块 product的路由:module\product\product-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import {ProductComponent} from './product.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path:'',
component:ProductComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forChild(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class ProductRoutingModule { }product的模块:
import { ProductRoutingModule } from './product-routing.module';
imports: [
ProductRoutingModule
],user模块
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import {UserComponent} from './user.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path:'',
component:UserComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forChild(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class UserRoutingModule { }user的模块
import {UserRoutingModule} from './user-routing.module'; +
imports: [
UserRoutingModule +
],RouterModule.forRoot() 和 RouterModule.forChild()
RouterModule对象为提供了两个静态的方法:forRoot()和forChild()来配置路由信息。
RouterModule.forRoot()方法用于在主模块中定义主要的路由信息,RouterModule.forChild()与 Router.forRoot()方法类似,但它只能应用在特性模块中。
即根模块中使用forRoot(),子模块中使用forChild()。
配置子路由
在商品模块的路由product-routing.module.ts 配置子路由
import { PlistComponent } from './components/plist/plist.component';
import { CartComponent } from './components/cart/cart.component';
import { PinfoComponent } from './components/pinfo/pinfo.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path:'',
component:ProductComponent,
children:[
{path:'cart',component:CartComponent},
{path:'pcontent',component:PinfoComponent}
]
},
{path:'plist',component:PlistComponent}
];在商品模块的模板product.component.html 添加router-outlet
<router-outlet></router-outlet>在页面app.component.html添加菜单,方便跳转
<a [routerLink]="['/product']">商品模块</a>
<a [routerLink]="['/product/plist']">商品列表</a>Ngxs 状态管理
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f343b8bca096
https://blog.csdn.net/roamingcode/article/details/84568140
https://blog.csdn.net/fen747042796/article/details/74840844
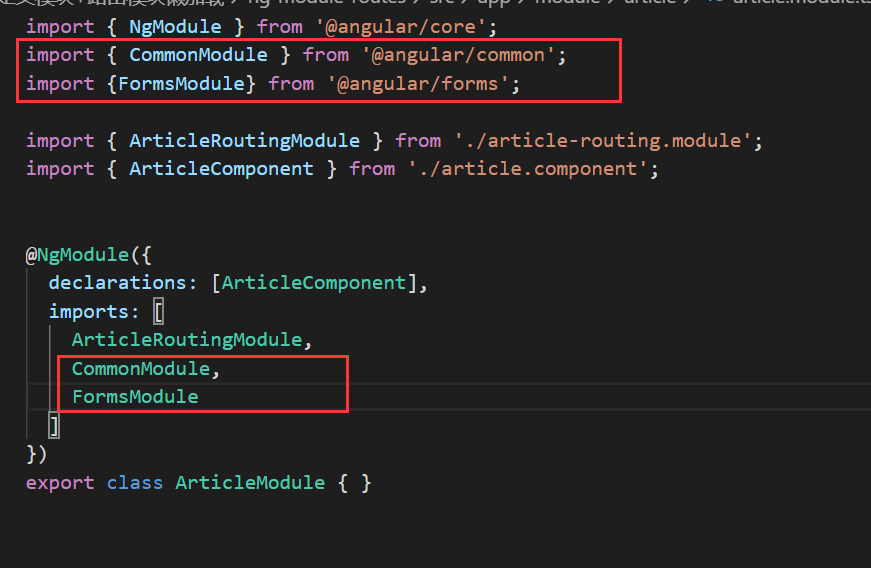
问题: The pipe 'async' could not be found?
@NgModule 的申明没有被子模块继承, 如果你在子模块中需要管道 pipe , directives, components, 在子模块里应该 再次导入需要的模块
这个 pipes 都是来自于 CommonModule
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
@NgModule({
imports: [ CommonModule ]
})
class ArticleModule {}为什么在 app.component组件可以工作, 是因为 你已经导入了 BrowserModule ,BrowserModule又重新导出了 CommonModule, 所以只需要导入 BrowserModule 就间接的导入了 CommonModule
同样值得注意的是,CommonModule也有核心指令,比如ngFor和ngIf。因此,如果您有一个使用这些功能的功能模块,则还需要将CommonModule导入该模块